* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Organelles Worksheet
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
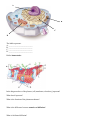
Cellular Structure and Function Cell Theory: What are the three parts of the cell theory? Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes: Fill the Venn diagram for the following cell structures and organelles: cytoplasm, DNA, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, ribosome, lysosome, mitochondria, nucleus, plasma membrane, vacuoles. Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Animal and Plant Cells. Use the following terms to fill in the Venn diagram for animal and plant cells: cell wall, centrioles, chloroplasts, cytoplasm, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, mitochondria, nucleus, plasma membrane, large vacuole . Animal cells Plant cells Is the diagram below an animal or a plant cell? How can you tell? A B C D The labels represent: A: ___________________________ B: ___________________________ C: ___________________________ D: ___________________________ Define homeostasis: In the diagram above of the plasma (cell) membrane, what does j represent? What does f represent? What is the function of the plasma membrane? What is the difference between osmosis and diffusion? What is facilitated diffusion? How does active transport differ from passive transport? Organelles: Complete the following table by writing the name of the cell part or organelle in the right hand column that matches the structure/function in the left hand column. A cell part may be used more than once. Structure/Function 1. Stores material within the cell 2. The sites of protein synthesis 3. Transports materials within the cell 4. The region inside the cell except for the nucleus 5. Organelle that manages or controls all the cell functions in a eukaryotic cell 6. Contains chlorophyll, a green pigment that traps energy from sunlight and gives plants their green color 7. Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria 8. Small bumps located on portions of the endoplasmic reticulum 9. Firm, protective structure that gives the cell its shape in plants, fungi, most bacteria and some protists 10. Produces a usable form of energy for the cell 11. Packages proteins for transport out of the cell 12. Site where ribosomes are made 13. The membrane surrounding the cell 14. Name for the collection of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells 15. Consist of hollow tubes which provide support for the cell 16. Composed of a phospholipid bilayer 17. Storage for nutrients and water in plant cells How does exocytosis differ from endocytosis? Cell Part An investigation was set up to study the movement of water through a membrane. The results are shown in the diagram. Based on these results, which statement correctly predicts what will happen to red blood cells when they are placed in a beaker containing a water solution in which the salt concentration is much higher than the salt concentration in the red blood cells? a. The red blood cells will absorb water and increase in size. b. The red blood cells will lose water and decrease in size. c. The red blood cells will first absorb water, then lose water and maintain their normal size. d. The red blood cells will first lose water, then absorb water, and finally double in size. For beakers 1-9, the particle size of the solute is able to diffuse through the semi-permeable membrane. Indicate in the table below, in which direction the solute and water will move (into the bag, out of the bag, no net movement). 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Solute movement Water movement 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 For cells 10-18, the particle size of the solute is not able to diffuse through the semi-permeable membrane. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 17. 18. 16. In the table below, indicate how water moves (into the bag, out of the bag, no net movement). Where the percent of the solute or water is not given, complete the number in the table. Water movement 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 % water in the bag % water out of the bag % solute % solute in the bag out of the bag Type of Solution