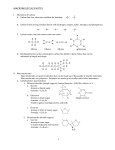
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Micro Lab Unit 1 Flashcards
Survey
Document related concepts
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Lab 4 Macromolecule Flashcards What are the four classes of large organic molecules found in living things? (also called macromolecules) What is each macromolecule composed of? In macromolecules, what are the identical or similar subunits called? What does the characteristic shape and organization of a macromolecule determine? What class of macromolecules are carbohydrates? What is the range in size of a carbohydrate? What is another name for a carbohydrate that contains a single monomer? What is another name for a carbohydrate that contains two monomers? What is another name for a carbohydrate that contains many monomers? What is glucose? What is the body's main preferred source of fuel for cellular respiration? As glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream, how soon can it be used for cellular respiration? If glucose is not immediately used for cellular respiration, what happens to it? What is the only nutrient utilized as a source of energy by the tissues and brain? In plants, what is glucose used to form? Where are excess sugars in plants stored? What is the most abundant structural polysaccharide in plants? Generally, what source of carbohydrates is not usable to most animals? What is a major component of the cell wall of a plant? What are polymers of amino acids? What is the body's least preferred source of energy? Why is protein one of the body's least preferred sources of energy? Why are proteins essential? What are the three components that make up a nucleotide? In a nucleotide, what happens when the sugar and phosphate component bind together? 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic acids Many identical or similar subunits bound together Monomers Their function Sugars Single monomer to large/complex polymer Monosaccharide Disaccharide Polysaccharide Monosaccharide derived from sugar Glucose Immediately Gets stored as glycogen in the liver or skeletal muscles Glucose Various storage or structural polysaccharides As starch in the roots and other tissues Cellulose Cellulose in plants Cellulose Proteins Protein They are expensive to construct, used for other metabolic processes, and are important to the body For biochemical reactions, necessary for metabolic processes to take place and are integral to the structure of DNA, muscles, and heart 1. nitrogenous base 2. pentose sugar 3. phosphate group Forms a backbone for the nucleotide Lab 4 Macromolecule Flashcards What is DNA? What does DNA stand for? What is RNA? What does RNA stand for? What are lipids not a true class of macromolecules? What are lipids composed of? What four things are classified as lipids? What are fats stored in the body as? What is used as a second source of energy for metabolic processes? What do you add to test for the presence of simple sugars in Macromolecules? What result will it give you when you add Benedict Solution to something that contains sugar? What to do you add to test for the presence of starch in Macromolecules? What result will it give you if the starch is present? What do you add to test for the presence of fats in Macromolecules? What result will it give you when fat is present? What do you add to the presence of protein in Macromolecules? What color will it change it to when protein is present? What color will it change to in the presence of amino acids? What are the building blocks for carbohydrates? What are the building blocks for proteins? What are the building blocks for nucleic acids? Are fats true polymers? If Iodine was added to a test tube and resulted in an amber color, what can you conclude? What chemical indicator would you use to test the presence or absence of protein? What is a chemical indicator? If you were testing an unknown sample with Benedict’s and Biuret solutions that resulted in a red and bluish color respectively, what can you conclude about what is in the sample? Double stranded helical structure that contains genetic information Deoxyribonucleic acid Single stranded nucleic acid that is involved in the synthesis of proteins and the genome of some viruses Ribonucleic acid They do not form polymers Carbon and hydrogen atoms 1. fats 2. phospholipids 3. waxes 4. steriods Triglycerides Fats Benedct;s Solution It will change to green, yellow, orange, red or rust color Iodine (IKI) Iodine will change to navy blue/black color Sudan Red color Biuret Purple/lavender color Pink color