* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide for Exam II
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive evolution in the human genome wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
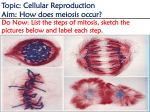
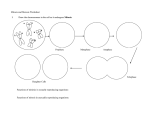
Study Guide for Exam IV Fall 2009 ** Note: This is simply a tool to help you study. The information below might not include ALL of the topics you will be responsible for. Anything covered in lecture or lab is fair game. Genes/Inheritance With what organism did Mendel famously experiment? What is Mendel’s law of Segregation? What is a gene? What is an allele? What is it that genes do? What is a trait? What are the possible relationships between genes and traits? What is the difference between homozygous and heterozygous? What is the difference between a dominant and recessive allele? What is incomplete dominance? What is a Punnett square, and how is one used? What do the terms ‘genotype’ and ‘phenotype’ mean? Why are dominant genetic disorders less common than recessive ones? Why don’t recessive genetic disorders get “weeded out” over time? Why don’t dominant genetic disorders get “weeded out” over time? If a green frog (Gg) was crossed with a yellow frog (gg), how many genotypes and phenotypes would there be? If both parents are carriers for Sickle-cell Anemia, what are the odds that their baby will have the disorder, be a carrier, or not have any sign of the disease? What is a pedigree chart? (know how to read one) Meiosis – one cell splitting into 4 genetically different cells Steps: prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, telophase II What occurs in each step? In what ways is meiosis I different than meiosis II? In what ways is meiosis different than mitosis? What is the difference between a haploid and diploid cell? What are chromatids? Where in the human body does meiosis occur? Evolution What is the definition of a species? What is a gene pool? What is the definition of evolution? Why would it be incorrect to say that evolution is always moving organism toward a more perfect form? What are some other common misconceptions about evolution? What is the ultimate cause of new traits developing in a population (variability)? What is the difference between Natural Selection and Genetic Drift? What is the difference between analogous and homologous structures? In terms of Natural Selection, what does the "fittest" mean? What is "speciation"? Besides Geographical Isolation, what are other reasons that cause speciation to occur? Can migration cause evolution? How do the Peppered moths illustrate evolution by natural selection?