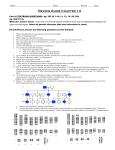
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Last Year`s Exam 2
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
DiGeorge syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Down syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Inversion Probe wikipedia , lookup
Name __________________________________ ID _________________________________ PSYC 3102: Intro to Behavioral Genetics (Carey) Exam 2 Multiple Choice The purpose of linkage analyses is to: a) determine the exact location of a gene b) determine the approximate location of a marker c) determine the approximate location of a gene d) determine the exact location of a marker e) none of the above _____ An RFLP is: a) a Repetitive Family Linked Polymorphism b) a Ribosomal Fat LipoProtein c) a Recombination Frequency Linkage Probe d) a Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism e) a Repetitive Frequently Linked Primer _____ A karyotype is: a) an observable phenotype b) an observable genotype c) monosomy of a chromosome d) a picture of stained chromosomes e) trisomy of a chromosome _____ Down’s syndrome is characterized by: a) Alzheimer’s-like pathology b) abnormal fingerprints and palmprints c) protruding mouth d) increased leukemia risk e) all of the above _____ A DCG is: a) a Disease with CG repeats b) a Disorder with Chromosomal Gaps c) a Disorder with Complex Genetics d) a Disease that is Completely Genetic e) none of the above _____ A major locus for a disorder: a) determines whether or not a person will get the disorder b) causes a phenocopy _____ c) is a marker used in linkage analyses d) is a Mendelizing form of the disorder e) has a relatively large effect on the disorder Individuals with William’s syndrome tend to: a) have an elfish appearance b) have impaired non-verbal abilities c) have normal verbal abilities d) have musical ability e) none of the above _____ Mendel’s law of segregation states that: a) some hereditary factors dominate others b) each parent passes 1 of 2 hereditary factors at random to offspring c) linked loci are transmitted as a unit d) hereditary factors for one trait are transmitted independent of those for another trait e) all of the above _____ Prader-Willi syndrome: a) is caused by the same chromosomal abnormality that causes Angelman’s Syndrome b) is caused by inheritance of a microdeletion from the father c) is characterized by obesity due to overeating d) is due to genomic imprinting e) all of the above _____ A probe: a) carries a light bulb b) binds with its complementary sequence c) is single-stranded d) identifies a match between the probe and RNA (or DNA) e) all of the above _____ A Turner’s Syndrome individual has the karyotype: a) 47XYY b) 45XO c) 46XX d) 47XXY e) 45YO _____ Which of the following is NOT a type of polymorphism? a) RFLP b) SNP c) variable number of tandem repeats d) insertion e) none of the above _____ Genetic linkage was first described by: a) Mendel b) Morgan c) Galton d) Watson e) Crick _____ True/False Familial AD is associated with early onset. _____ A man with genotype AO at the ABO locus has the blood type (phenotype) A. _____ XXY males are hypermasculinized and aggressive. _____ Prader-Willi and Angelman’s Syndromes result from deletions of the same chromosomal segment. _____ The best predictor of Down’s syndrome is paternal age. _____ The frequency of chromosomal disorders at fertilization is about 10% _____ 100% of AD cases are accounted for by APP, presenilin 1, presenelin 2, and ApoE4. _____ An extra or missing autosome is usually ok. _____ Fill in the Blank The technique ____________________ is used to amplify DNA. If two loci are rarely separated by recombination, then they are ____________________. The “gold standard” for diagnosing AD is identification ____________________ and ____________________. The karyotype ____________________ characterizes a normal male. ____________________ is the major disadvantage of population-based association studies. ____________________ is the progressive and irreversible loss of intellectual function. The process of making double-stranded DNA single-stranded is called ____________________. *** I have removed the Short/Long Answer portion, in case Dr. Carey decides to use the same questions, but here are the basics of those questions: Know how to give the genotypes, phenotypes, and frequencies for a given cross (know how to do a Punnett square and give results) What is the meaning of 1p15.33? Know what PCR, RFLP, and SNP stand for and what they are and what their significance is Know: Alzheimer’s disease; restriction enzymes and function; electrophoresis; and polymorphisms