* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetic Disorders - Learn District 196
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Down syndrome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
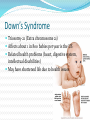
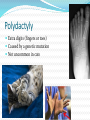
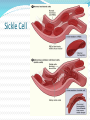
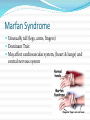
A genetic disorder is a condition caused by abnormalities in genes or chromosomes. Most disorders are rare and affect 1 in hundreds of thousands or millions A genetic disorder is not always detrimental Alibinsm Symptoms Absence of color in the hair, skin, or iris of the eye Lighter than normal skin and hair Patchy, missing skin color Cause: Inheritance of 2 mutated genes (rare) In animals, survival of albinos is challenging Dwarfism Most forms of dwarfism have a genetic basis. Most cases (75-90%) of achondroplasia, however, are the result of sudden mutations of a chromosome. For this reason, most achondroplastic dwarves are born to normal parents. There is a 25% chance that two achondroplastic dwarves would give birth to a normal child, and it is also possible for two achondroplastic dwarves to conceive a doubledominant child, where both parents pass on the gene for achondroplasia. This condition is fatal, and results in a miscarriage or a very short lifetime for the child. Down’s Syndrome Triosomy-21 (Extra chromosome 21) Affects about 1 in 800 babies per year is the US Related health problems (heart, digestive system, intellectual disabilities) May have shortened life due to health issues Hemophilia Blood does not clot normally (coagulation) A sex linked recessive disorder More common in males than females Female is more likely to be a carrier Polydactyly Extra digits (fingers or toes) Caused by a genetic mutation Not uncommon in cats Klinefelter’s Syndrome XXY Genotype (XY is normal) Due to nondisjunction during meiosis Individual is most likely infertile Affects about 1 in 1000 males XXX Syndrome Trisomy X Syndrome is due to nondisjunction during meiosis Results in extra chromosome Affects about 1 in 1000 females No readily observable abnormalities Sickle Cell Blood cells are shaped like crescents instead of round This causes problems with circulation and the bloods ability to carry oxygen Recessive gene. Parent may be a carrier for sickle cell (have the trait but not the disease) May have life long pain, fatigue. No cure at this time Sickle Cell Marfan Syndrome Unusually tall (legs, arms, fingers) Dominant Trait May affect cardiovascular system, (heart & lungs) and central nervous system Colorblindness Most color blindness is due to a genetic problem. About 1 in 10 men have some form of color blindness. Very few women are color blind. Lactose intolerance (Galactosemia) Disorder due to a genetic mutation Individual unable to produce lactase (enzyme that aids in breaking down lactose (milk sugar) Turner Syndrome Unpaired X chromosome Many associated health and reproductive problems Huntington’s Disorder Huntington's disease, chorea, or disorder (HD), is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects muscle coordination and leads to cognitive decline and dementia Caused by a gene mutation Symptoms may not appear until later in life.