* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Natural Selection - wvhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
Survey
Document related concepts
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
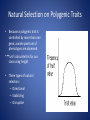
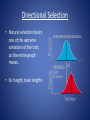
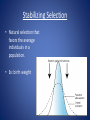
Evolution Chapters 16 & 17 Darwin’s Voyage Chapter 16 Evolution • Change over time Charles Darwin • Developed a scientific theory that explains how modern organisms evolved over long periods of time through descent from common ancestors. Darwin’s Voyage • 1831: Darwin sailed around the world in the HMS Beagle making observations and collecting evidence. • Most of his work was done at the Galapagos Islands, located 100 km west of South America. • 1859: Darwin publishes Origin of the Species. Darwin’s Observations 1.) Different, yet similar, animal species inhabited separated, but similar, habitats around the globe. 2.) Different, yet related, animal species occupied different habitats within a local area. 3.) Some fossils of extinct animals were similar to living species. Ideas that Shaped Darwin Public Perception • All life was only a few thousand years old. • Since its creation, not much had changed. Scientists that Influenced Darwin • (1785) James Hutton: Using geological examples, concluded that the earth must be much older than a few thousand years. • (1798) Thomas Malthus: Reasoned that if the human population grew unchecked, their wouldn’t be enough space and food for everyone. • (1830) Charles Lyell: Argued for uniformitarianism, which holds that the geological processes we see today must be the same ones that occurred long ago. Jean Baptiste Lamark • (1809) Published a theory on evolution that suggested organisms could change during their lifetimes by selectively using or not using parts of their bodies. These acquired traits could then be passed onto their offspring. • What is wrong with this theory??? Natural Selection Words to Know fitness: the ability to survive and reproduce adaptation: an inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s chance of survival • Adaptations increase an organism’s fitness. Natural Selection • AKA: survival of the fittest • Selected traits increase an organism’s fitness. • No human involvement. (Unlike selective breeding.) For Natural Selection to Occur: 1. The population must be limited in size, which creates competition. (Competition: when two organisms want the same resource at the same time.) 2. Genetic variation (of inherited traits) must exist. Sources of Variation 3. This variation must affect the organism’s reproductive success. Recipe for Evolution Descent with modification • Species descend from other species over time. Ex: dogs descended from wolves. Common descent: all things, living and extinct have common ancestors Evidence of Evolution Evidence of Evolution 1. Structural adaptations A. Mimicry: one species resembles another species B. Camouflage: species blend in with surroundings Evidence of Evolution 2. Behavioral adaptations a. Migration b. Courtship c. Defending or claiming territory d. Cooperation (Ex: hunting in packs) e. Kin selection: helping a relative survive because they share the same genes f. Communication (visual, chemical, sound, language) More evidence… 3. Fossils 4. Geographic Distribution of Species (similar, but unrelated species live in different parts of the world) And more evidence… 5. Homologous structures: basic arrangement of bones in body structures of different species is similar ex: bird wing and whale flipper Note: Not to be confused with analogous structures (have the same function, but different structures) And more evidence… 6. Vestigial structures: body structures that serve no purpose in the present day organism ex: an ostrich’s wings And more… 7. Similarities in early development. 8. Biochemistry: comparing the DNA and RNA All Living Things are Related Evolution Misconceptions Evolution of Populations Chapter 17 Populations, NOT individuals evolve! Gene pool: all of the alleles of a population’s genes Relative frequency = # certain allele x 100% total # alleles Ex: attached earlobes ***Let’s calculate this for our class! Genetic equilibrium: when the relative frequency remains the same over several generations • If the relative frequencies in a gene pool change, EVOLUTION has probably occurred! Sexual vs. Asexual Reproduction • The two main sources of genetic variation in sexually reproducing organisms is through mutations and genetic recombination. • The main source of genetic variation in asexually reproducing organisms is through mutations only. Natural Selection on Single Gene Traits 12 14 10 12 10 8 Hands Up 8 Hands Up Hands Down 6 Hands Down 6 4 4 2 2 0 0 Before the Predator After the Predator Natural Selection on Polygenic Traits • Because a polygenic trait is controlled by more than one gene, a wide spectrum of phenotypes are observed. ***Let’s calculate this for our class using height. • Three types of natural selection: – Directional – Stabilizing – Disruptive Average Height 7 6 5 4 Average Height 3 2 1 0 150 160 165 170 180 cm cm cm cm cm Directional Selection • Natural selection favors one of the extreme variations of the trait, so the entire graph moves. • Ex: height, beak lengths Stabilizing Selection • Natural selection that favors the average individuals in a population. • Ex: birth weight Disruptive Selection • Individuals with either extreme variation are selected for. (The average drops.) • Ex: Light and dark colored limpets Speciation • Occurs when members of the same population can no longer interbreed to produce fertile offspring. • Can occur from geographic, behavioral or reproductive isolation. Divergent vs. Convergent Evolution Divergent evolution: Convergent evolution: members of one species members of different become less and less species evolve similar alike, eventually traits because of their resulting in separate environment. species The Effect of Small Populations Genetic drift: a change in allele frequencies due to something other than natural selection Ex: Ashkenazi Jews, the Amish, the Holocaust Specific types of genetic drift are… Founder effect: a small group starts a new population elsewhere and their particular genes become prevalent Bottleneck effect: a natural disaster drastically reduces the population