* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 - CSU, Chico
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
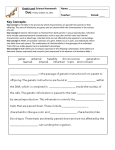
Survey of Physical Anthropology Exam 1 1. Anthropology can be thought of as ____________ because it _________. a. being holistic; recognizes the complex interactions of everything that made us what we are as a species b. interdisciplinary; draws knowledge from many areas of study c. biocultural; looks at the interactive relationships of human biology and culture d. both A and B e. All of the above 2. Two subfields of physical anthropology include __________ which includes people who specialize in __________ and __________ whose members study__________. a. Ethnography, describing cultures; ethnology, cross-cultural differences b. CRM, legal archaeology; medical anthropology, how cultures deal with disease c. Primatology, non-human primate behavior; osteology, skeletal biology d. Applied, real-life applications; ethnoastronomy, how people perceive the stars e. Forensic, identifying skeletal remains for law enforcement; lingustic anthropology, the evolution of language and its implications to culture 3. Two subfields of cultural anthropology include __________ which includes people who specialize in __________ and __________ whose members study__________. a. Ethnography, describing cultures; ethnology, cross-cultural differences b. CRM, legal archaeology; medical anthropology, how cultures deal with disease c. Primatology, non-human primate behavior; osteology, skeletal biology d. Applied, real-life applications; ethnoastronomy, how people perceive the stars e. Forensic, identifying skeletal remains for law enforcement; linguistic anthropology, the evolution of language and its implications to culture 4. As defined in class, all anthropologists can be described as seeking to investigate humanity’s ___, __, and __. a. adaptive significance, heritage, direction b. variation, evolution, adaptation c. economy, culture, psyche d. life, history, biology e. society, psychology, sociology 5. To practice good scientific method, a careful researcher will (in sequential order) seek to: a. develop a theory about observations, test that theory, and then develop a hypothesis to explain the results b. notice something of interest in the world, develop a hypothesis, state a law c. analyze data, draw conclusions, win a Nobel prize d. be creative, employ skepticism, develop a hypothesis e. develop a hypothesis about observations, test that hypothesis, develop a theory out of the results obtained if the hypothesis is not disproven 6. The Use/Disuse ideas from LaMarck are also called the Principle of Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics. a. True b. False 7. The idea that the world’s population must have some kind of limiting factors (competition) of some kind or there would soon be greater population than the carrying capacity of the planet could hold is called _____________ and is best associated with ______________. a. Superposition; Ray b. Exponential Growth; Malthus c. Teleology; Watson and Crick d. Uniformitarianism; Lyell e. Unitarianism, Rev. Sun Yung Moon 8. Two early ideas about the organization of life in the world were ________ which was the idea that all life was organized into some hierarchical structure with humans at the top, and _______________ which stated that once created, all species were forever unchanging. a. Teleology, Fixity of species b. The Great Chain of Being, Fixity of Species. c. Taxonomy, Great Chain of Being d. Fixity of Species, Teleology e. None of the above 9. Which of the following was NOT an influence on Darwin? a. Malthus b. Lyell c. Mendel d. A and B e. B and C 10. Darwin believed that Natural Selection worked to create new species through the accumulation of changes within an ancestor species over relatively short periods of time (two to three generations). a. True b. False 11. A mathematical expression of the likelihood of an animal with a certain variant of a trait to survive and reproduce is called _____________. a. Hardy-Weinberg b. Fitness c. Selective Pressure d. Crossing Over e. None of the above 12. Because there is great redundancy in the number of codons, simple substitution mutations are less likely to have dramatic effect. a. True b. False 13. The function of tRNA is to carry the message of the DNA from the mitochondria to the nucleus, wherein proteins are built from free-floating enzymes. a. True b. False 14. In a non-disjunction error such as Trisomy 21, there has been a failure of one or more chromosome pairs to fully split during one of the stages of meiosis. a. True b. False 15. A fertilized egg is called a : a. Gamete b. Codon c. Enzyme d. Zygote e. None of the above 16. DNA and RNA are both nucleic acids. a. True b. False 17. The first 22 pairs of numbered chromosomes are termed the autosomes. a. True b. False 18. Proteins are actually formed from long chains of: 2 a. b. c. d. e. Nucleic Acids Amino Acids Base Pairs Enzymes None of the above 19. In a cross between parents who are both heterozygous for a trait, how many offspring will be heterozygotes? a. 0% b. 25% c. 50% d. 75% e. 100% 20. Which of the following is NOT a possible offspring from the following mating: AaBbCCDd X aaBBCcDd? a. aaBBCCDD b. AaBbCCdd c. AABBCCDD d. Both a and b e. All of the above are impossible offspring 21. In the offspring of two individuals who are both heterozygous for a single trait, what is the phenotype ratio? a. 1:2:1 b. 1:2:1:2:4:2:1:2:1 c. 3:1 d. 9:3:3:1 e. None of the above 22. Nuclear DNA is found in __________. a. The nucleus of the cell b. In chromosomes c. Ribosomes d. A and B e. B and C 23. One complete nucleotide consists of ______________, _____________, and ____________. a. Ribose, Protein, Sodium Pentathol b. Deoxyribose, a phosphate, one of four amino acids c. Ribose, a phosphate, one of four nucleotide bases d. Deoxyribose, a sugar, one of three triplet codons e. Deoxyribose, a phosphate, one of four nucleotide bases 24. DNA is a special molecule because it can ____________ and it _________________. a. Self-replicate, contains the coding for all proteins in the body b. Leave the nucleus, creates amino acids at the Golgi apparatus c. Destroy invading microbes, contains the coding for mitosis d. Metastasize, alleviates stress holistically e. None of the above. DNA can do none of these things. 25. In cellular divisions, _____________ is responsible for the creation of new ________. a. Meiosis, gametes b. Mitosis, somatic cells c. Meiosis, eggs and sperm d. Mitosis, non-reproductive body cells e. All of the above are true 3 26. In cellular division, the final “daughter cells” produced through meiosis will have ______ chromosomes within them, which is ________ the number as the “parent cell”. a. 23; half b. 92; double c. 23; double d. 46; the same e. 46; double 27. A sequence of three bases in the DNA chain is called a __________. a. Replicant b. Codon c. Mutation d. Segregation e. Ribosome 28. Which of the following is an example of a Mendelian trait in humans? a. Sickle-cell anemia b. ABO blood type c. Rh blood type d. Achrondroplasia (genetic dwarfism) e. All of the above 29. In DNA, the nucleotide base _________ will only pair with ___________. a. Adenine; Guanine b. Protein; Cytosine c. Uracil; Guanine d. Thymine; Adenine e. Thymine; Guanine 30. PCR is a process used to forcibly replicate strands of DNA. a. True b. False 31. Mendelian traits are those which ______________ such as ___________. a. Are controlled by multiple alleles at multiple loci; height and weight b. Are controlled by alleles at a single locus; height and weight c. Only have a single allele; the presence of five fingers on the hand d. Are controlled by two or more alleles at a single locus, the ABO blood system e. None of the above. 32. Traits which are non-discrete (they have a continuous distribution of phenotypes), and are controlled by alleles at more than one locus are called: a. Mendelian b. Evolutionary c. Polygenic d. Monozygotic e. Dizygotic 33. Which of the following is not true of Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)? a. Does not undergo recombination b. Is passed only through the maternal lineage c. Can be used to suggest population relationships d. Is of little use to anthropologists e. Is found outside the nucleus of the cell 34. Some factors which alter allele frequencies in a population include: __________. 4 a. b. c. d. e. Mutation Natural Selection Genetic Drift Gene Flow All of the above affect allele frequencies 35. Which of the following would be the best population for studying genetic drift? a. A very small hippie commune with rapidly changing membership b. A farmer’s large herd of cattle with equally large numbers of males and females c. The survivors of Chernobyl after the meltdown of its nuclear plant d. European immigrants flooding in during the early part of this century e. Survivors of a shipwreck (assuming they interbred) 36. Sickle Cell Anemia is an example of a: a. balanced polymorphism b. trait in which heterozygotes have advantages over homozygotes c. trait with no anthropological or evolutionary significance d. A and B e. All of the above 37. The drug Rhogam is given to women in order to suppress their immune systems and make conception more likely to occur since the body’s chemistry is altered to make it more receptive to sperm. a. True b. False 38. A man is questioning that a particular child is his. If the child is type O and the mother is type A, then which of the blood types below would the man need to be in order to exclude himself from the list of potential fathers with 100% probability? a. A b. B c. AB d. O e. The man is unable to exclude himself as the father with a simple blood test. 39. People who are blood type O are referred to as universal donors since they make both types of antigen on the surfaces of their red blood cells. a. True b. False 40. You are blood type O; you can accept a transfusion from type(s): a. A b. B c. AB d. O e. All of the above 41. A type of mutation in which a single point in the series of bases is replaced with an alternate base is called: a. insertion b. deletion c. substitution d. crossing over e. None of the above 42. The sickle cell allele, when found in the homozygous condition, causes the disease known as Malaria. a. True b. False 5 Matching Concepts Match the following terms with the most appropriate associated idea or definition. There is only one correct response for each term. Be careful, if you miss one here, you likely just missed two! 43. 44. 45. 46. Gene Flow Genetic Drift Chromosome Locus 47. Codon A. Long strand of DNA macromolecules B. Position of a gene on a chromosome C. Sequence of three nucleotides D. Migration or exchange of genes between populations E. Affects only small populations through random fluctuations in allele frequency Matching People From the pedigree above, please answer the next three questions. 48. The trait represented is inherited as a(n): a. Polygenic b. Autosomal Dominant c. Autosomal Recessive d. Sex-linked Recessive e. Sex-linked Dominant 49. The genotype of individual “A” is: a. AA b. Aa c. aa d. AA or Aa e. The trait is sex linked 50. The genotype of individual “B” is: a. AA b. Aa c. aa d. AA or Aa e. The trait is sex linked 6