* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3: Equations - Math Specialist Aman
Survey
Document related concepts
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
Functional decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Recurrence relation wikipedia , lookup
Numerical continuation wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Vincent's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic reciprocity wikipedia , lookup
Hyperreal number wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of algebra wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic form wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
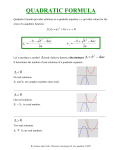
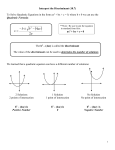
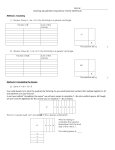
Unit 3: Quadratic Equations Unit Review Topics Covered: 1. Factoring GCF Difference of Squares Easy and Hard Trinomials Substitution 3 and 1 Grouping 2. Solving Equations by Factoring 3. Solving Equations by Completing the Square 4. The Quadratic Formula: x b b 2 4ac 2a 5. The Discriminant: b 2 4ac If b 2 4ac > 0, we have 2 different real roots If b 2 4ac = 0, we have 2 equal real roots If b 2 4ac < 0, we have no real roots Homework: p. 242-248 Examples: 1. Factor a) 8 y 2 22 yx b) x 2 (b a) 4(b a) c) 5 x 4 80 d) x 2 12 xy 20 y 2 e) 3x 2 10 x 8 f) 2a 5 26a 3 72a g) 12 x 3 6 x 2 y 18xy2 h) (3a 5) 2 (a 3) 2 i) (2 x 1) 2 5(2 x 1) 6 j) k) x 2 9 5 x 2 2 1 2 2 1 x x 5 15 3 l) x 2 10 x 25 z 2 2. Solve by completing the square: a) 2 x 2 12 x 5 b) 2 x 2 10 x 5 3. Solve. You may use the quadratic formula if appropriate: a) (2 x 1)( x 3) ( x 2) 2 b) x 27 3 x 4. Find the value of the discriminant, then state the nature of the roots: a) 3 x 2 5 x 2 b) 4 x 2 12 x 9 5. Find k so that the following has no real roots: 5 x 2 kx 3 0 6. A stone is thrown off of a 30 m cliff. It’s height is given by the formula: h 4.9t 2 10.5t 30 . How long does it take to reach the bottom of the cliff? 7. When 3 times a number is subtracted from the square of the number the result is 28. Determine the number 8. Two numbers have a sum of 20 and a product of 84. Determine the numbers.