* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reflexes
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Electromyography wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
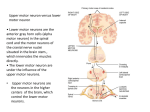
Reflexes I. General a. Description b. Components: i. receptor, ii. sensory neuron, iii. integration center- generally within CNS; may involve simply a synapse (monosynaptic) or may involve interneurons (polysynaptic) iv. motor neuron v. effector c. Somatic reflexes involve skeletal muscle responses; when they occur, the cerebral cortex will be notified and you will be aware of the event! Visceral reflexes involve ANS effectors (ex, smooth muscle) and the cerebral cortex will not necessarily be notified. II. Somatic Spinal Reflexes: 2 specific examples to know a. The stretch reflex -monosynaptic -receptors are specialized muscle cells embedded within whole muscles: intrafusal muscle fibers -sensory neurons monitor the degree (type Ia fibers and type II fibers) and rate of stretch (type Ia fibers) of the intrafusal muscle fibers -the whole production (receptor cells and sensory neuron endings) is called a muscle spindle -when the muscle is stretched, sensory neurons send impulses and “tell” motor neurons to activate their muscles. This increases tone of the muscle and prevents over-stretching. -the stretch reflex is accompanied by a reflex that causes antagonistic muscles to relax (reciprocal inhibition). b. The withdrawal (flexor) reflex -polysynaptic -also accompanied by reciprocal inhibition reflex III. Visceral Reflexes- will be covered with the ANS!