* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review L14 Gene to Protein L15 Gene Reg
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
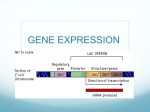
Review Questions - Lecture 14: Gene to Protein 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. What is the difference between genotype & phenotype? What is gene expression? Why is the phrase “one gene, one protein” inaccurate? Provide a definition for transcription and translation that clearly distinguishes between the two terms. What is a codon? Why is redundancy important in codons? Make a series of drawings that clearly shows what happens in each step of transcription (initiation, elongation and termination). Be sure to include the following: promoter, RNA polymerase, nucleotides, transcription factors, TATA box, polyadenylation signal sequence). 8. What are the cap and tail added to mRNA made of? What are their function? 9. Make a drawing that clearly shows RNA splicing. Include: introns, exons, splicesome. 10. What are ribozymes? 11. Make a series of drawings that clearly shows what happens in each step of translation (initiation, elongation and termination). Be sure to include the following: tRNA, anticodon, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, small and large ribosomal subunits, A-site, P-site, exit site, mRNA binding site, start tRNA, codon recognition, peptide bond formation, growing peptide chain, translocation, stop tRNA, release factors. 12. What are polyribosomes? 13. What happens to the polypeptide chain after it is synthesized? 14. How do proteins that should be made in the ER get to the ER? 15. Make a list of all the different types of RNA and their functions. 16. What is a mutation? 17. What is a point mutation? 18. Distinguish between the following types of mutation: silent, missense and nonsense. 19. How are insertions and deletions different than base-pair substitutions? 20. What are some causes of mutations? 21. Do all mutations that occur get passed on to offspring? Review Questions - Lecture 15: Gene Regulation, Part 1 1. 2. 3. 4. Describe how feedback inhibition works. Draw a picture of an operon, including: promoter, operator, genes. What is a regulatory gene? Make a series of drawings that compares/contrasts a repressible operon and an inducible operon. Include: promoter, operator, genes, repressor, corepressor, regulatory gene, RNA polymerase, inducer, mRNA. 5. What is the difference between negative gene regulation and positive gene regulation? 6. Make a series of drawings showing a combination of negative and positive gene regulation in the lactose metabolic pathway. Include: promoter, operator, genes, repressor, regulatory gene, RNA polymerase, inducer, mRNA. CAP, cyclicAMP, activator, glucose concentration, CAP-binding site.