* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lecture 17
Survey
Document related concepts
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Peer-to-peer wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
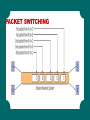
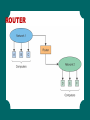
TELECOMMUNICATION & NETWORK APPLICATIONS PART 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Benefits of telecommunication networks in business Networking basics: Architecture, Topology, Protocols, Media Network applications COMPUTER NETWORKS Connected computers: Work together Are interdependent Exchange data with each other SIZE OF COMPUTER NETWORKS Home computer network Global computer network National computer network MOBILE COMPUTING The characteristics, mobility and broad reach, create five value-added attributes that break the barriers of geography and time: • • • • • Ubiquity : regardless of user’s location Convenience Instant connectivity Personalization Localization of products and services Ubiquity: mobile device can provide information and communications regardless of user’s location. Convenience and Instant Connectivity: Internetenabled mobile device makes it easy and fast to access the Web, intranets, and other mobile devices without booting up a PC or placing a call. Personalization: information can be customized and sent to individual consumers (e.g., as a short message service). Localization of products and services: knowing a user’s location helps companies advertise their products and services. BENEFITS OF A CONNECTED WORLD Networks offer many advantages for a business including • Sharing resources • Providing opportunities • Reducing travel Before networks, transferring data between computers was time-consuming and labor intensive. People had to physically copy data from machine to machine using a disk. Networks offer many advantages for a business including: Sharing resources Providing opportunities Reducing travel There have been many network security problems - networks are a tempting target for mischief and fraud An organization has to be concerned about… Proper identification of users and authorization of network access The control of access, and the protection of data integrity CHALLENGES OF A CONNECTED WORLD Networks have created a diverse, yet globally connected world by eliminating time and distance, networks make it possible to communicate in ways not previously imaginable Even though networks provide many business advantages, they also create increased challenges in • Security • Social, ethical, and political issues BENEFITS OF BUSINESS MOBILITY Enhance mobility Provides immediate data access Increases location and monitoring capability Improves work flow Provides mobile business opportunities Provides alternative to wiring CHALLENGES OF BUSINESS MOBILITY Protecting against theft Protecting wireless connections Preventing viruses on a mobile device Addressing privacy concerns with RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and LBS (Local Base Service) TYPES OF NETWORKS A computer network is a system that connects computers via communications media so that data can be transmitted among them. • • • • Local area networks Wide area network Value-added network Enterprise network Local area networks: connects two or more devices in a limited geographical region. Wide are network: networks that cover large geographical areas. Value-added network: a type of wide area network that are private, data-only networks managed by third parties that provide telecommunication and computing services to multiple organizations. Enterprise network: the entire network of an organization, usually consisting of multiple local area networks and multiple wide area networks. LOCAL AREA NETWORK WIDE AREA NETWORK ENTERPRISE NETWORK HUMAN COMMUNICATION COMPUTER COMMUNICATION Senders and Receivers There must a be a sender and a receiver with something to share via a message to facilitate communication Communication Medium (Channel) A medium must exist between the sender and receiver over which the message travels (e.g., a cable) Protocols Procedures, rules, or standards must be followed by computers when sending or receiving data CODING, SENDING, DECODING THE TELECOMMUNICATIONS SYSTEM A telecommunications system consists of hardware and software that transmit information from one location to another. TYPICAL TELECOMMUNICATIONS SYSTEM ANALOG AND DIGITAL SIGNALS COMMUNICATIONS PROCESSORS Modem – Modulation/Demodulaion: covert analog signals to digital signals and vice versa Multiplexer – a single channel can carry data simultaneously from many sources Front-End Processor – mainframe communicates with many computers Modem: device that converts digital signals to analog signals and vice versa. Multiplexer: an electronic device that allows a single communications channel to carry data transmissions simultaneously form many sources. Front-End Processor: a specialized computer that manages all routing communications with peripheral devices. Modems Digitizing (change info to bits 0-1) Modem Modulator/Demodulator -(code/decode digital/analog) BASIC NETWORKS PERSONAL AREA NETWORK Personal area networks (PAN) - Provide communication over a short distance that is intended for use with devices that are owned and operated by a single user Bluetooth - Wireless PAN technology that transmits signals over short distances between cell phones, computers, and other devices WIRELESS LAN Wireless LAN (WLAN) - A local area network that uses radio signals to transmit and receive data over distances of a few hundred feet Wireless fidelity (Wi-Fi) - A means by which portable devices can connect wirelessly to a local area network, using access points that send and receive data via radio waves WIRELESS MAN Wireless MAN (WMAN) - A metropolitan area network that uses radio signals to transmit and receive data WIRELESS MAN Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access (WiMAX) - A communications technology aimed at providing high-speed wireless data over metropolitan area networks WIRELESS WAN CELLULAR Wireless WAN (WWAN) - A wide area network that uses radio signals to transmit and receive data WIRELESS WAN CELLULAR Smart phone - Offer more advanced computing ability and connectivity than basic cell phones 3G - A service that brings wireless broadband to mobile phones Streaming – A method of sending audio and video files over the Internet WIRELESS WAN SATELLITE Satellite - A space station that orbits the Earth receiving and transmitting signals from Earth-based stations over a wide area NETWORK BASICS Networks are differentiated by the following: • Architecture - peer-to-peer, client/server • Topology - bus, star, ring, hybrid, wireless • Protocols - Ethernet, Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) • Media - coaxial, twisted-pair, fiber-optic PROTOCOLS Protocol - A standard that specifies the format of data as well as the rules to be followed during transmission Interoperability - The capability of two or more computer systems to share data and resources, even though they are made by different manufacturers ETHERNET Ethernet - A physical and data layer technology for LAN networking TRANSMISSION CONTROL PROTOCOL/ INTERNET PROTOCOL TCP/IP applications • • • • File transfer protocol (FTP) Simple mail transfer protocol (SMTP) Hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) Simple network management Protocol (SNMP) NETWORK PROTOCOLS Rules or procedures used to transmit and receive data Specify: • Connection of computers to the network • Error checking • Data compression • Signal of finished transmission • Signal of received message Examples of protocols: • OSI, TCP, IP, UDP, IPX, SPX, etc. THE FOUR LAYERS OF THE TCP/IP PROTOCOL ARCHITECTURE There are two primary types of architectures • Peer-to-peer (P2P) network • Client/server network PEER-TO-PEER NETWORKS Peer-to-peer (P2P) network - Any network without a central file server and in which all computers in the network have access to the public files located on all other workstations CLIENT/SERVER NETWORKS Client - A computer that is designed to request information from a server Server - A computer that is dedicated to providing information in response to external requests • Client/server network - Model for applications in which the bulk of the back-end processing takes place on a server, while the front-end processing is handled by the clients CLIENT/SERVER NETWORKS Network operating system (NOS) - The operating system that runs a network, steering information between computers and managing security and users Packet-switching - Occurs when the sending computer divides a message into a number of efficiently sized units called packets, each of which contains the address of the destination computer Router - An intelligent connecting device that examines each packet of data it receives and then decides which way to send it onward toward its destination CLIENT/SERVER NETWORKS PACKET SWITCHING PACKET SWITCHING ROUTER ROUTER THANKYOU