* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10 the internet and the new information technology infrastructure
Survey
Document related concepts
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
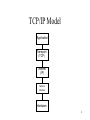
10 THE INTERNET AND THE NEW INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY INFRASTRUCTURE 1 The New IT Infrastructure • Large DBs that need central storage found on mainframes, or specialized servers. Smaller DBs and portions of larger ones on PCs/Workstations • Client/server computing is used to distribute power to desktop • Extend to desktop to includes mobile devices • Incorporates public infrastructure (telephone system, Internet, etc.) 2 IT Infrastructure • Enterprise Networking – An arrangement of the organization’s hardware, software, network and data resources – To put power on the desktop & create a company-wide network linking smaller networks • Internetworking – Linking of separate networks, each of which retains its identity, into an interconnected network 3 Standards and Connectivity • Connectivity – The ability of computers and computer-based devices to communicate and share information without human intervention • Open Systems – Software that operates on different hardware – Built on application standards, and network protocols 4 Model of Connectivity • TCP/IP (Transmission control protocol/internet protocol) – Used in the Internet, allows different types of computers to communicate – Five layers • OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) – Seven layers, international reference model • Bluetooth – Allows high-speed, radio-based communication – Used with wireless devices, over small area 5 TCP/IP Model Application Transport (TCP) Internet (IP) Network Interface Hardware 6 Client/server Computing on the Internet 7 Internet Capabilities • E-mail – Person -to-person messaging; document sharing • Usenet Newsgroups – Discussion groups using electronic bulletin boards • List Servers – Discussion groups using email list servers • Telnet – Working on one computer while logged on to another • FTP – Transfer of files from computer to computer • World Wide Web – Display, format and retrieve information using hyperlinks • Chat Rooms – Interactive conversations 8 Domain Names •Example: www.chaudhury.mis.umb.edu •Equivalent IP: 158.121.112.98 Root .mil .net .com .edu .org .umb .cs .mis .chaudhury .kuilboer • Domain name – Unique name to identify a node on the Internet – Corresponds to an IP address – Domain Name Server (DNS) maps domain names to their IP address – Contains sub-domains, separated by periods 9 Top level domains Domain Description com Commercial, business edu Educational gov Government mil Military net ISP or other network services provider org Not-for-profit organization ca, uk, is, it Country indicators Other domain names have been approved (e.g., biz, info, name, museum) 10 Next Generation Internet • Internet2 – Research network with new protocols and transmission speeds – Supports high bandwidth applications – Video portal – CA*net3: Canada’s Internet2 11 Searching the Web • Search Engine – A tool for locating specific sites on the Internet • Bots/Agents – Software tool that facilitates digging through data (e.g. a shopping bot) • Broadcast and “Push” Technology – Computer automatically broadcasts information to user based on preferences 12 Intranets & Extranets • Intranet – Private network using Internet technology – Protected from outsiders by firewalls • Hardware and software placed between intranet and external networks • Packet Filtering router: submits packets to filter that applies a set of rules • Extranet – Intranets that allow authorized access by external stakeholders (e.g., suppliers, customers) 13 Wireless Web • Wireless Web Standards – WAP (wireless application protocol) • Uses WML (wireless markup language) • Optimized for tiny displays (e.g. cell phones) – I-mode • Developed in Japan, being introduced in Europe and NA • Uses compact HTML (easier to integrate than WML) 14 Organizational Benefits of Internet & Web • Provide global connectivity • Reduce communication and transaction costs – Email, Internet telephony (Voice over IP) – Enhance coordination and collaboration • Accelerate the distribution of knowledge • Enhance customer relationship and supply chain management 15 E-commerce & e-Business Technologies • E-commerce server software – – – – – – – Set up storefronts and catalogues Design electronic shopping carts Make shipping arrangements Link to electronic payment systems Display product availability & tracking Connect to back-office systems Report on site statistics and functions 16 Customer Tracking & Personalization Tools • Goals of tracking and personalization tools – Collect and store data on behaviour of online customers – Analyze data to better understand behaviour – Identifying customer trends • Clickstream tracking – Tracking customer activities, storing in a log • Collaborative filtering – Compare customer tracking data with data from customers with similar profiles, predict preferences 17 Web Management • Content management tools – Facilitates collection, assembly and management on a web site • Web performance monitoring tools – Monitors download times, transaction times, broken links and bottlenecks • Web hosting Services 18