* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rome: From Kingdom to Republic
Survey
Document related concepts
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Switzerland in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Elections in the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
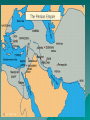
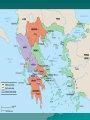
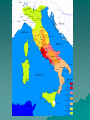
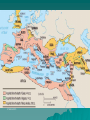
Classical Mediterranean Mediterranean Traditions Persian Greek / Hellenistic Roman Persian Empire (Achaemenid) ~550 BCE - ~330 BCE Established by Cyrus the Great, great King Darius, capital at Persepolis Modern day Iran/Afghanistan/Pakistan regions Neighbor and rival of Greek city states (Persian wars ~500-450 BCE) Political Styles – Tolerance for other cultures – Authoritarianism – Infrastructure, especially roads – Bureaucracy Advanced iron technology Unique artistic style Zoroastrianism Overthrown by Alexander the Great Later Sassanid Empire (227 CE – 600s CE) during Roman period preserves Persian culture The Persian Empire Zoroastrianism Monotheistic religion (the first? Judaism ~1200s BCE) Emerged as early as 1700 BCE, codified by Zoroaster/Zarathustra (c. 630-550 BCE) Gathas – sacred literature Ahuramazda – creator and benevolent deity Angra Mainyu (evil spirit) Magi – religious priests Cosmic struggle between good and evil, humanity punished or rewarded in afterlife for their actions Religious justification for political rule Civilization in Mediterranean Region Greeks began with city-states due to geography (mountains & coast) Oceanic trade on Mediterranean Sea connected the region Both Greece and Rome created empires based on conquest.. Phoenecian Greece cultural influences (alphabet, seafaring) Mycenaen Kingdom (~1400 BCE) – Culture preserved in Homer’s epics Iliad & Odyssey Greek city-states (polis) develop 800600 BCE – Mountains & coastlines help fragment Greece & prevent political unity – Trade, commerce, and connections b/n citystates helps develop a common “Greek” culture (similar language, alphabet, religion, Sparta –vs- Athens Sparta – military aristocracy conquers and controls neighboring regions (slavery) Athens – commercial, diverse, also used slaves, artistic and intellectual achievements, limited democracy allowed adult male citizens to select officials and pass laws (Pericles 400s BCE) Persian wars (common enemy) ~500s-450 BCE Peloponnesian Wars (431-404 BCE) b/n Athens and Sparta Greece and Greek Colonies, c. 431 B.C.E. The Hellenistic Period Phillip II of the northern kingdom of Macedon conquered Athens and Sparta and gained control of the Greek peninsula (330s BCE) His son Alexander (the Great) extended the empire as far as the borders of India Alexander died young and his empire was divided into several Hellenistic Kingdoms for the next few centuries. Greek culture spread throughout the Mediterranean world and Middle East during this “Hellenistic” Era Alexander’s Empire and the Hellenistic World, c. 323 B.C.E. Greek (Hellenistic) Civilization in Mediterranean, 240 BCE Patterns of Greek and Roman History Rome – Roman Republic from 509 B.C.E. Military emphasis Punic Wars, against Carthage (264-146 B.C.E.) – Empire Julius Caesar victory over rivals, 45 B.C.E. Augustus Caesar, rules from 27 B.C.E. Empire strong to about 180 C.E. Renewed vigor under Diocletian, Constantine STEA63540075 Greek and Roman Political Institutions Greece – The Polis – Athens - direct democracy – the assembly Lottery for positions Citizen body a minority of the population – Most city states were oligarchies Aristocratic Sparta assemblies Greek and Roman Political Institutions Rome – Balance – Senate – dominated by aristocrats – Consuls – Dictator Greek and Roman Political Institutions Political Theory in Ancient Greece and Rome – Duties of citizens, political ethics, oratory – Participation stressed – Comparison of the merits of different forms – Romans developed law code Twelve Tables, by 450 B.C.E. Law comes to take the place of fathers Spread of code to empire, and citizenship Greek and Roman Political Institutions Roles of Government – Public works Help to unite empire – Maintaining law courts, police power – Official religion Religion and Culture Religious Values – Religion largely concerned with the here and now – Mystery religions offered a more spiritual approach – Division between elite and popular belief Religion and Culture Philosophy – Provided a system of ethical behavior – Aristotle, Cicero Stressed balance – Stoics stress inner life Religion and Culture Science and Philosophy – Socrates – encouraged questioning – Speculation on the physical world Theories matter about the universe, the nature of – Mathematics, especially geometry – Hellenistic period More empirical work in physics Euclid, Galen Religion and Culture The Arts – Drama: comedy and tragedy Balance between virtue and emotions Sophocles Oedipus the King – Epics, the Iliad, Odyssey – Architecture – Roman engineering Economy and Society in the Mediterranean Agriculture and Trade – Constant trend to market farming Led to trade Grain from Egypt – Merchants Officially, legally respected Not socially esteemed Economy and Society in the Mediterranean Slavery – From conquest – Becomes a motive for expansion – Technological innovation in farming lacking Unfavorable trade balance with eastern Asia Economy and Society in the Mediterranean Family – Patriarchal – Women have economic role Some women active in commerce Women could own property A Complex Legacy What Survived? –Enduring ideas –No polities –Direct and indirect Consciously imitated, revived Mingled with Middle Eastern legacy Global Connections: Persia, Greece, Rome, and the World Persia – Maintained contact between East and West Greece – Traders, expansionist – Alexander the Great New contacts between Mediterranean, Persia, India Rome – Variety of contacts Detailed info on Roman politics Roman Republic & Constitution Roman nobility established a republic in 509 BCE Built Roman Forum = political and civic center Republican constitution Executive responsibilities in 2 Consuls – Held civil & military power – Consuls elected by assembly of aristocrats (patricians) – Senate of aristocrats advised Consuls & ratified decision Most prominent political & military leaders Largely controlled Roman public affairs Mostly served interests of the wealthy Plebians (commoners) objected > class conflict – Plebians given more rights in 5th & 4th BCE – Patricians still dominated Rome Dictator wielded absolute power for 6 months if “military crisis” Expansion of the Republic Rome surrounded by invaders Rome first established a large regional state in Italy Roman control of entire Italian peninsula (4th century BCE) – Established military colonies – Generous policies toward conquered peoples Taxes, local rule, and trade were established Conflict and conquest in larger Mediterranean – Punic wars with Carthaginians (N. Africa) Destroyed Carthage, took slaves, took “stuff” – Conflict with Greeks 5 major wars Controlled most of the Med. By 2nd BCE The Failure of the Republic Warfare and territorial expansion undermined the foundations of the Roman Republic Wealth and power were increasingly concentrated in the hands of the upper classes, resulting in the decline of the peasant farmer / soldier class. The military became increasingly loyal to their commanders, as opposed to the Senate. Some of these generals used their armies to increase their own personal power and wealth, at the expense of the state. The Formation of the Roman Empire By 31 BCE, Octavian (heir of Julius Caesar), had eliminated all rivals and seized power. Known as Augustus, he was the first of the Roman Emperors. Subtly concentrated power in his hands, while maintaining the appearance of the Republic. Allied himself with the Equities – the second most powerful group below the Senatorial class. Roman Civilization STEA63540075