* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Roman Empire
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Berber kings of Roman-era Tunisia wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
First secessio plebis wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Romanization of Hispania wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Elections in the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman technology wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
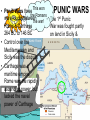
The Roman Empire Brief History (625 BCE - 23 BCE) Rome (as a city) founded circa 625BCE The Roman Republic (510 BCE - 23 BCE) lasted for over 500 years Citizens elected Senators Senate chose a consul (who ruled like a King) for 1 year. No Tyrants, deferred to the Senate. Way of Life - The Roman Republic • 4 Classes of people in Roman society. 1. Slaves - lowest class, no rights, owned by other people. 2. Plebeians - free people, but had little input. Way of Life - The Roman Republic 3. Equestrians (a.k.a. 'knights'). Their name means the 'riders', as they were given a horse to ride if they were called to fight for Rome; had to be rich. 4. Patricians - nobles, very wealthy, held all the power, members of the senate. I make it rain!!!!! Pax Romana (27 BCE - 180 CE) • The Roman Peace – Considered to be the “height” of the Roman Empire. – Ruled by Caesars or emperors. • Senate exists but its power is limited. • Period of great territorial expansion; architectural innovation in Rome; and wealth. The Movie - Gladiator • Begins with the death of Marcus Aurelius (180 CE) who had wanted the reign of the emperors to end and the Senate to rule Rome as it had been during the Roman Republic. Themes: – “Absolute power corrupts absolutely” (as with all tyrants and eventually with corrupt politicians) – The Masses (plebeians) needed to be appeased gladiator blood sport where they decided gladiator’s life or death often served as diversion/appeasement away from political discontent. – All roads led to Rome and all roads in Rome led to the Coliseum. • Punic Wars three This won the Romans wars fought between the war! • Rome & Carthage 264 BC to 146 BC • Control over the Mediterranean and Sicily was the dispute • Carthage was a maritime empire, Rome was the rapidly ascending power, but lacked the naval power of Carthage PUNIC WARS The 1st Punic War was fought partly on land in Sicily & Africa but was mostly a naval war. It began as a local conflict in Sicily. Romans added the corvus, an assault bridge, to Roman ships. The hinged bridge would swing onto enemy vessels with a sharp spike and stop them Second Punic War • Remembered for the Carthaginian Hannibal’s crossing of the Alps. • Rome took countermeasures against Hannibal's home base in Africa by march sea command & stoppedWethe flow of to Rome!! supplies. Hannibal quickly turned back & rushed home but was defeated in battle. • (149–146 BC) involved an extended siege of Carthage • three-year siege before he breached the walls, sacked the city, and systematically burned Carthage to the ground in 146 BC 3RD Punic War Essential Question: Before the Movie Imagine our freeways and highways, when exiting, what do you generally see no matter what exit you take? What, in your opinion, does this say about our society? Essential Question: After the Movie You learned last week that terrorism is 100% ineffective - terrorists always end up strengthening the very “thing” they are targeting. Oppression, corruption, terror, and enslavement were characteristic of the ancient great empires (Greek and Roman) and modern imperialist/colonial periods (1600s-1900s) of the European Monarchies/Democracies. Describe how did Maximus’s character exemplified/symbolizes the outcome - that terror, enslavement, and oppression is 100% ineffective (over the long term).