* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animal behavior Unit
Social psychology wikipedia , lookup
Attitude change wikipedia , lookup
Prosocial behavior wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Impression formation wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
Social perception wikipedia , lookup
Organizational behavior wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Transtheoretical model wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Social cognitive theory wikipedia , lookup
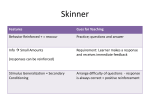
Chapter 34 Notes Animal Behavior (Ethology) Behavior – an organism’s reaction to changes in its internal condition or external environment. Anything an animal does in response to environmental stimulus. • Example: Stimulus Presence of peahen Change in daylength Heat of the desert sun Movement of potential prey Response peacock displaying colorful tail whales wintering in S. Calif. lizard seeking shade tiger shark swimming toward movement Inherited Behavior - behavior patterns that are genetically programmed. p.873 1.) Innate behavior (inborn behavior) • Inherited behavior of animals, fully functional on first performance. (mammal nursing/ spider web weaving) • Consisting of automatic response and instinctive behavior. A.) Automatic response (quick) • Reflex – simple response; no conscious control. • Fight or flight – mobilizes the body for greater activity (fight or run) B. Instinctive behavior (complex pattern) • Courtship behavior – species recognition. • Territoriality – physical space defended. • Aggressive behavior – growling/teeth baring. • Migration – seasonal movement cycle of animals. • Hibernation – physiological change that reduces an animal’s need for energy. • Circadian rhythms – sleep at night, awake during day for example. Learned Behavior (Acquired behavior) p. 873 Learned Behavior – behavior patterns that develop/change over time through practice/experience. 1. Habituation : stimulus repeatedly given not associated with punishment or reward; eventually animal ceases to respond to stimulus. 2. Classical Conditioning: learning by association; Pavlov’s dog experiment. 3. Operant Conditioning (Trial and Error Learning): Learning in which an animal receives a reward for a particular response; motivation commands quicker learning. First described by B.F. Skinner, American psychologist; Invented the “Skinner Box” around 1930. 4. Insight: Learning based on previous experience when responding to a new situation. Experimental example: a hungry chimpanzee was able to reach bananas suspended overhead by stacking boxes on top of one another, then climbing the stack and successfully feeding. • Imprinting: occurs at a specific critical time in life; social attachment established. Imprinting is believed to be unchangeable once it has occurred. • Involves both innate and learned behavior. • Imprinting example: Newly hatched ducks/geese learn to recognize/follow the first moving object they see, usually their mother. • Ivan Pavlov, Russian physiologist, 1900; won the Nobel Prize in 1904. • B.F. Skinner, American psychologist; Invented the “Skinner Box” around 1930.