* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Missouri secession wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
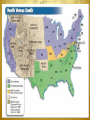
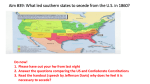
Texas Secession Essential Questions: Define characteristics of the Civil War & Reconstruction Era. Explain the significance of 1861. Explain reasons for the involvement of Texas in the Civil War such as states’ rights, slavery, sectionalism, tariffs, and secession. Main Idea: Abraham Lincoln was elected president in 1860. In 1861, Southern states, including Texas, formed the Confederate States of America. Many Issues Divide the Country Tariffs – taxes on trade 1828 “Tariff of Abominations” (a high tax) South hated it Forced to sell cotton @ low prices to be competitive Pay high prices for North manufactured goods “Nullification Crisis” Results South Carolina believed that states had the right to nullify a federal law it considered unconstitutional. South Carolina threatened to secede but a compromise ended the threat. This issue continued to brew until 1861. Many Issues Divide the Country Sectionalism – loyalty to the interests of one's own region or section of the country, rather than the nation as a whole Many Texans came from southern states and grew the chief cash crop, which was cotton. Texas resembled the economy, social structure, customs, and political values of the South which concentrated on plantation agriculture, slave labor, and the Democratic Party. Many Issues Divide the Country States Rights – Texans believed that states should be able to make their own political, economic, and social decisions. Slavery – Texans believed that slavery was vital to the economy; opposed Republican Party b/c most members did NOT want to see slavery spread to new territories Southern Society in 1850s Upper Class – Slave Elite Middle class – Few Slaves Lower Class – No Slaves Lower Middle Class – 1 or 2 Slaves Slaves Southern States Vow to Secede During the 1860 presidential campaign, Southerners warned that they would secede if the Republicans won. Lincoln was Republican candidate that won the election Secession: Southerners argued that sovereignty rested with the states, saying the states entered the Union voluntarily and could likewise leave. The Convention Votes on Secession Governor Sam Houston opposed secession by declaring that Texas could be better protect its interest by staying in the Union. “South can’t win the war” Texans favoring secession called a convention. The Texas Secession Convention met in Austin in January 1861. They adopted the Ordinance of Secession, which declared that the U.S. abused its power to “strike down the interest and prosperity of the people of Texas.” Sam Houston Quote #1 “Let me tell you what is coming. After the sacrifice of countless millions of treasure and hundreds of thousands of lives you may win Southern independence, but I doubt it. The North is determined to preserve this Union. They are not a fiery, impulsive people as you are, for they live in colder climates. But when they begin to love in a given direction, the move with the steady momentum and perseverance of a mighty avalanche.” The Convention Votes on Secession On February 23, 1861 the people of Texas approved secession by a wide margin. Texas became the seventh state of eleven to secede from the U.S. and form a new country in the South. The Confederacy is Formed The 7 seceded states met at a convention in Montgomery, Alabama, and formed a new nation called the Confederate States of America (C.S.A.) and drew up a constitution. First Confederacy Flag The states were given more power, the federal government less, and the constitution guaranteed the protection of slavery. The document replaced references to the U.S. with references to the Confederacy. Houston is Removed When the Texas Secession Convention ordered all states officials to take an oath of allegiance to the Confederacy, Houston refused and was removed as governor. President Lincoln offered Houston the use of federal troops if he would oppose the convention that voted for secession, but, unwilling to cause a civil war in Texas, Houston refused. Governor Sam Houston Sam Houston Quote #2 “Would you be willing to deluge [flood] the capital of Texas with the blood of Texans, merely to keep one poor old man in a position for a few days longer, in a position that belongs to the people? No! . . . Go tell my deluded friends that I am proud of their friendship, of their love and loyalty, . . . [but] to go to their homes and to conceal from the world that they would have been guilty of such an act.” The War Begins President Lincoln believed the C.S.A. had no right to leave the Union. He vowed to preserve the nation and carry out the law of the land in all states. Battle of Fort Sumter A “perpetual” Union On April 12, 1861, Confederate troops opened fire on U.S. troops at Fort Sumter in Charleston, South Carolina, starting the Civil War.