* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Civil War
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fredericksburg wikipedia , lookup
Battle of White Oak Road wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cumberland Church wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Appomattox Station wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Donelson wikipedia , lookup
Kentucky in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Galvanized Yankees wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
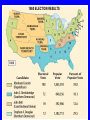
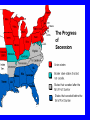
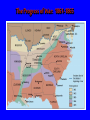
Civil War United States History Mrs. O’Shea 1860 Presidential Election • • • • Abraham Lincoln won 39% popular vote 180 electoral votes not a single electoral vote from South Name did not appear on many southern ballots 1860 ELECTION RESULTS Southern Secession South Carolina seceded in Dec. 1860 6 others states followed = Texas Louisiana Mississippi Alabama Florida Georgia Created Confederate States of America Fort Sumter • Federal fort outside Charleston, SC • Federal supply ship shot at by Confederates • Lincoln wanted to preserve Union – must protect fort • April 12, 1861 – Confederates seize fort • Lincoln called on loyal states to supply 750,000 militiamen to subdue the rebellion. • Ordered blockade of southern ports. Battle of Bull Run • Union troops – not prepared • Sent by Lincoln to capture Richmond – Confederate capital city • Met with 32,000 Confederate troops outside of Manassas. • Union troops were sent running back to Washington, D.C. IMPORTANCE • Boosted Confederates morale • Signaled to Union that they needed to prepare for a real war CASUALTIES • Heavy casualties on both sides – killed, wounded, captured, or MIA • Disease (typhoid fever, dysentery, salmonella, gangrene, malaria) Casualties (deaths) Revolutionary War = 4,400 Mexican American War = 13,000 Civil War = 600,000 WWI = 115,000 WWII = 407,000 Korean War = 33,000 Vietnam War = 58,000 War in Iraq = 4,244 (as of February 13, 2009) Really rough estimates – Mrs. O’Shea Casualties (deaths) 700,000 600,000 600,000 500,000 Deaths 407,000 400,000 300,000 200,000 100,000 115,000 33,000 58,000 4,750 4,400 13,000 0 R o ev n io t lu y ar e M ar W n a xic ic an Am er ar W C ivi ar lW W W I W W II Ko an e r ar W V am n t ie W ar i r a W n q rI a Lincoln and Slavery • “Preserve the Union” • Personally opposed to slavery • Came to regard abolishing slavery as a strategy for winning war • Slave working in field = one more Southerner fighting in fields Emancipation Proclamation p. 396 • effectively removed any chance of a negotiated settlement between the North and the South. • The Emancipation Proclamation caused an outcry to rise from the South who said that Lincoln was trying to stir up slave rebellion. • The North now had a much stronger moral cause. It had to preserve the Union and free the slaves. African Americans in War • July 1862 – Congress allows African-Americans to join military • January 1, 1863 – Emancipation Proclamation – encouraged freed slaves to fight • By 1865 – 180,000 African Americans had enlisted (10% of troops) • Less pay • Black regiments – white officers • 54th Massachusetts Infantry – bravery in attack on Ft. Wagner – first medal of honor (Sergeant William Carney) GLORY Plans to Win!!! • Union – attacked from West and East – Anaconda Plan (choke them) • Confederacy – attacked Union through Virginia (scare Northerners – fuel anti-war movement in North) Advantages – pages 662-664 North South Advantages Economic and Military North South Gettysburg Address • • • • Dedication of cemetery Honors Union soldiers Expresses grief of nation Necessity of preserving the Union http://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php ?storyId=1512410 North – Strategy Anaconda Plan – General Winfield Scott Slowly entwine and crush Antietam “Bloodiest Single Day of the War” Union – McClellan CSA - Lee Maryland September 17, 1862 Results The result of the battle was inconclusive but the north did win a strategic advantage. 23,100 casualties Significance Forced the Confederate Army to retreat back across the Potomac River. President Lincoln saw the significance of this and issued the famous Emancipation on September 22, 1862. Chancellorsville Union – Major General Joseph Hooker CSA – Robert E. Lee, Major General Thomas J. Jackson Results Confederate Victory. 24,000 casualties of which 14,000 were Union soldiers. Significance Considered to be Lee’s greatest victory Death of Stonewall Jackson. Shiloh – “place of peace” Tennessee Union - Ulysses S. Grant CSA – Johnston Results Grant was defeated 20,000 casualties on both sides Draft Confederacy 1862 – ages 18-35 1862 – ages 18-45 1864 – ages 17-50 Exemptions – substitute or $500 in cash Union 1863 – ages 20-45 Exemptions - $300 or medical grounds NYC Draft Riots, (July 13-16, 1863) The Progress of War: 1861-1865 Sherman’s “March to the Sea” through Georgia, 1864 “War is cruelty. The crueler it is, the sooner it will be over.” Sherman’s March p. 412 • Union General William Sherman’s total war • GOAL = destroy the Confederacy's ability to wage further war • 300 mile path of destruction – destroying railroads, bridges, factories, livestock, crops, etc. • Most likely speed up the ending of the war South Surrenders Lee surrenders to Grant at Appomattox Court House, Virginia (private home – not a court building) -take horses and go home -obey laws April 9, 1865 Lincoln Assassinated • April 14, 1865 • John Wilkes Booth – wanted to kidnap in exchange for Confederate prisoners. • Changed plans – killed Lincoln • Ford’s Theater Execution