* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plasma Membrane
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
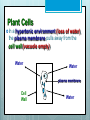
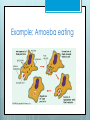
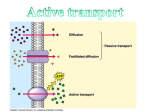
Active Transport Warm Up! Imagine that a human blood cell, which is 3% salt, is placed in a beaker of pure water. 1. 2. 3. Draw a picture of this scenario Is it in a hypertonic or hypotonic solution? Will it shrink or swell? Why? 3% Na 97% H2O solution 100% H2O Red Blood Cell Hypotonic Swell Animal Cells Animal cells placed into a hypotonic solution will EXPLODE. Hypotonic Red Blood Cell Animal Cells Animal cells placed into a hypertonic solution will SHRIVEL. Hypertonic Red Blood Cell Plant Cells In a hypotonic environment, the vacuole fills with water. Cell wall keeps it from exploding Water Cell Wall Water Central Vacuole Water Plant Cells In a hypertonic environment (loss of water), the plasma membrane pulls away from the cell wall (vacuole empty). Water Water plasma membrane Cell Wall Water To Do: Worksheet: “tonicity” Osmosis & Tonicity means predicting how a cell will react in a solution (hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic) Active Transport The movement of molecules across the plasma membrane using energy (ATP). ATP Adenosine triphosphate Made in the mitochondria Has high energy bonds Bonds can be broken to release energy for use in the cell 4 volunteers, please! When is Active Transport Needed? 1. Moving from LOW to HIGH concentration Called “against the concentration gradient” Requires Energy from ATP Ex: Protein pumps Some membrane proteins use energy to pump substances in and out of the cell. Volunteers, please! http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/9834092339/student_ view0/chapter5/sodiumpotassium_exchange_pump.html 2. Moving LARGE molecules into or out of the cell Example: Endocytosis ENTRY into cell Portion of the membrane surrounds or engulfs a large molecule outside cell. Requires Energy from ATP Types of Endocytosis Pinocytosis: endocytosis of liquids Phagocytosis: endocytosis of particles Example: White Blood Cell destroys bacteria Example: Amoeba eating Exocytosis: EXPORT of materials OUT of the cell (wastes, cell products) - Requires Energy from ATP Active Transport in the Human Body Protein Pump Nerve cells- Sodium Potassium Pump (electric signals) Pinocytosis Intestine cells absorb water/nutrients Egg cell absorbs water/nutrients Phagocytosis White Blood Cells (aka phagocytes) engulf & destroy bacteria, viruses, old cells Exocytosis Release digestive enzymes Release hormones Waste Closure Write out the KEY TERMS that you learned today!