* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
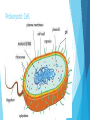
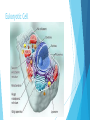
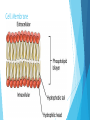
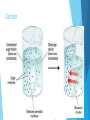
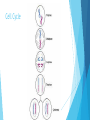
Cells Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells: These do NOT have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Only bacteria are prokaryotic. Eukaryotic cells: These do have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. These cells are larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells. Protists, Fungi, Plants, and Animals all have eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Plant vs. Animal Cells Plant cells have cell walls, plastids, and chloroplasts. Animal cells do not have these. Cell walls provide support for the plant. Plastids and chloroplasts allow plants to do photosynthesis. Animal cells have structures that help them move, called cilia and flagella. They also have centrioles, which help them during cell division. Cell Organelles Nucleus: contains the DNA. It is the brain of the cell. Golgi Apparatus: Sorts and packages proteins into transport or storage vesicles. (Post office of the cell) Cell Wall: rigid wall around cells that give shape and support. (NOT in animal cells) Cell Membrane: membrane around cell that allows things to pass through. (Gate keeper of the cell) Mitochondria: this is where cellular respiration takes place. (Energy maker of the cell) Cell Organelles Vacuoles: Storage sac for food and water. Cytoplasm: Jelly-like substance in the cell. Ribosomes: Make proteins. These can be free-floating or on Rough ER. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): These transport RNA and proteins. - Smooth ER: Does not have ribosomes on it. - Rough ER: Has ribosomes on its surface. Cell Transport Cell Transport How does stuff get in and out of the cell? Important Terms Solution: a liquid mixture of solute dissolved in solvent. For example, in salt water (salt is the solute and water is the solvent). Homeostasis: maintaining balance within the cell. Hormones: chemicals that regulate body functions. Cell Transport Cell Membrane: this membrane is semi-permeable (only certain substances can go through). The cell membrane is made of a phospholipid bilayer. Cell Membrane Passive Transport Passive transport: molecules move through the cell membrane from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration (this is called with the concentration gradient). This means that it will end with an equal amount of both sides when it reaches equilibrium. Types of Passive Transport Diffusion: Particles/substances move directly through the membrane. Facilitate Diffusion: Involves the help of a channel or carrier protein to move substance through membrane. This is typically used for large particles that won’t fit otherwise. Osmosis: Water moves through the membrane. Osmosis is the diffusion of water. Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis Types of Solutions Isotonic: particle concentration is the same outside and inside the cell. Hypotonic: particle concentration is lower in solution than inside the cell. Hypertonic: Particle concentration is higher in solution than inside the cell. Effect of Solutions on Cells Active Transport Active Transport: This requires energy. This is movement of substances from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Instead of trying to be equal on both sides, the cell is trying to get all of the substance on one side (either in or out of the cell). Types of Active Transport Exocytosis: this moves materials out of the cell. Endocytosis: this moves materials into the cell. Cellular Energy Photosynthesis Process of converting carbon dioxide, water, and light energy into oxygen and sugar. Plants, algae, and some bacteria can to do photosynthesis. Photosynthesis Happens in an organelle called a chloroplast. Therefore, only cells with chloroplasts will perform photosynthesis. Cellular Respiration The process of breaking down food to release energy. Anaerobic Respiration (AKA Fermentation) The process of sugars breaking down in the absence of oxygen. Comparing Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Function Energy Storage Energy Release Location Chloroplasts Mitochondria Reactants CO2 & H2O C6H12O6 & O2 Products C6H12O6 & O2 CO2 & H2O 6CO2 + H2O + light C6H12O6 + 6O2 C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + H2O + Energy Equations Cell Cycle The cell cycle is the sequence of stages through which a cell passes between one cell division and the next. Phases of the Cell Cycle Interphase= the cell spends most of its time in this phase. Interphase is divided into 3 phases: 1. G1: Period of cell growth. 2. S: Period when DNA is replicated. 3: G2: Period when cell prepares for division. Mitosis: Prophase: The nucleus organizes the chromatin material into chromosomes. Metaphase: The chromosomes line up in center of cell. Anaphase: Chromosomes separate and are pulled to opposite sides of cell. Telophase: Cell membrane begins to grow across center of cell between the two nuclei. Cytokinesis: division of cytoplasm. (This is not a phase of the cell cycle) Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis: Mitosis: PMAT Only happens in body (somatic) cells. This means every cell except the sex cells, which are sperm and egg cells. Cell Cycle Cell Cycle Cell Cycle The processes of mitosis and cytokinesis together are called cell division. The result of cell division is two new daughter cells that are identical to the parent cell, because they have the same DNA as parent cell.