* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1 - Red Hook Central Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Scattered disc wikipedia , lookup
Sample-return mission wikipedia , lookup
Exploration of Jupiter wikipedia , lookup
Kuiper belt wikipedia , lookup
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
Naming of moons wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Space: 1889 wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
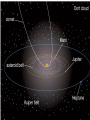
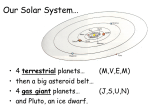
Formation of the Solar System Formation of the Solar System A model of the solar system must explain the following: 1. All planets orbit the sun counterclockwise 2. All planets orbit in about the same plane 3. Most planetary orbits are nearly circular 4. The distance between the planets increase in a regular trend with distance from the sun 5. Most planets orbit counterclockwise with little axis tilt (<25 degrees) 6. Almost all moons orbit in the same direction their planet rotates 7. Almost all moons orbit near their planet’s equatorial plane 8. The sun rotates in the same direction as the planets orbit (counterclockwise) Why is solar system so orderly? 2nd challenge: Why two types of planets? 1. Terrestrial/rocky: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars Small 2. Jovian/gas giants: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune large, Hydrogen-rich, many moons, rings of rock and ice 3rd Challenge: asteroids and comets • Asteroids mostly in asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter • Comets mostly in Kuiper Belt and Oort cloud 4th challenge: exceptions to the rule • Mercury has a more eccentric orbit • Mercury’s orbit is more inclined • Uranus’ axis of rotation is tilted almost on its side • Venus rotates backwards (clockwise) • Earth has a very large moon • A few Jovian moons orbit opposite direction from their planet’s rotation New stars like our sun, and their planetary systems, form from the gas and dust remains of older exploded stars. Flattening of planetary disk • • • • explains why: Planets all rotate in nearly the same plane Planets all orbit in same direction Most planets spin in the same direction Collisions within the disk tend to make elliptical orbits more circular Contraction: Interstellar cloud contracts due to gravity Cloud heats up, spins Condensation: Rocks and metals condense in inner solar system H and He gas collect to make gas giants Accretion: Materials collide and stick together Clearing: Other gases lost to space Leftovers become asteroids Comets, Kuiper belt Explaining the exceptions: • • Jovian planets captured some moons Giant impacts caused: 1. Earth’s large moon to break off from Earth 2. Backward rotation of Venus 3. Axis tilts of Earth and Uranus