* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Nervous System
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
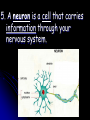
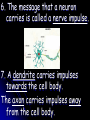
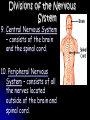
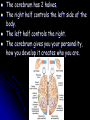
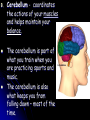
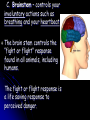
1. The function of the nervous system is to: Receive information about what is happening both inside and outside your body. 2. Stimulus - a change or signal in the environment that can make an organism react. Response - What your body does in reaction to a stimulus. Homeostasis – The process in which a living thing keeps it’s internal state normal despite it’s external environment. 3. Examples: Hunger, Thirst, ? 4. Your brain is an ORGAN and the nerves running through your body are tissues. 5. A neuron is a cell that carries information through your nervous system. Neuron Structure Neuron Structure 6. The message that a neuron carries is called a nerve impulse. 7. A dendrite carries impulses towards the cell body. The axon carries impulses away from the cell body. 8. 3 types of neurons 1. sensory – picks up stimuli from the internal or external environment. Ex: Hear cell phone ring. 2. interneurons – carries nerve impulses from one neuron to another. Ex: Carries message to brain 3. motor neuron – sends impulse to muscle or gland, and it reacts. Ex: Brain sends message to muscles in hand to pick up the phone. Divisions of the Nervous System 9. Central Nervous System – consists of the brain and the spinal cord. 10. Peripheral Nervous System – consists of all the nerves located outside of the brain and spinal cord. 11. The 3 Main Parts of the Brain A. Cerebrum – Interprets input from our senses and carries out tasks such as learning, thinking, remembering and making judgments. *Largest Part!* The cerebrum has 2 halves. The right half controls the left side of the body. The left half controls the right. The cerebrum gives you your personality, how you develop it creates who you are. B. Cerebellum - coordinates the actions of your muscles and helps maintain your balance. The cerebellum is part of what you train when you are practicing sports and music. The cerebellum is also what keeps you from falling down – most of the time. C. Brainstem – controls your involuntary actions such as breathing and your heartbeat. The brain stem controls the “fight or flight” response found in all animals, including humans. The fight or flight response is a life saving response to perceived danger. 12. The Spinal Cord The Spinal Cord is the only pathway between your brain and your peripheral nerves. 13. Your backbone (vertebrae) protect your spinal cord. If you broke your back and severed your spinal cord you will become paralyzed because your brain cannot get signals to your peripheral nerves. 14. The Peripheral Nerves The Peripheral Nerves are ALL of the nerves that lie outside of the brain and the spinal cord. All the nerves in your hands, feet, and mouth are controlled by peripheral nerves. **43 Pairs Reflex - an automatic response that occurs very rapidly without conscious control. Reflexes help to protect the body. Ex – Move hand away from hot object Duck if something is thrown at you Blink if something comes close to your eye Sneezing to clear airway