* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nazi Germany: 1933-1945 - Calvary Lutheran School
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
Kriegsmarine wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Britain (film) wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
United States Navy in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
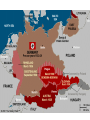
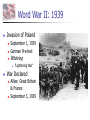
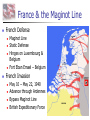
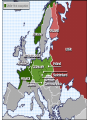
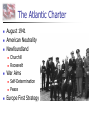
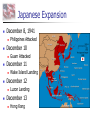
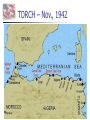
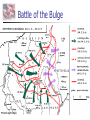
Nazi Germany: 1933-1945 Treaty of Versailles Rhineland - 1936 Austria – Anschluss -1938 Sudetenland - Czech - 1938 Czech Refusal – Threat of War Munich Conference September, 1938 France, Great Britain, Germany Appeasement: Sudetenland give to Germany Chamberlain and Churchill German Expansion 1936-38 Nazi Aggression Continues Czechoslovakia - 1939 Demand for Danzig European Response Germany City prior to WWI Great Britain & France Pledge to defend Poland Nonaggression Pact Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact Germany and Soviet Union August, 1939 Secret Agreement - Poland Word War II: 1939 Invasion of Poland September 1, 1939 German Pre-text Blitzkrieg “Lightening War” War Declared Allies: Great Britain & France September 3, 1939 Blitzkrieg in Poland Results Polish Defenses Overwhelmed Danzig falls on Sept. 7 Warsaw Capitulates Sept. 28 Opposition Ends on Oct. 6 65,000 Polish Troops Killed 100,000s Wounded/Captured Phony War German Conquests Grow British & French Mobilize German Conquests Churchill Denmark – April 1940 Norway – April 1940 Belgium, Luxembourg, Netherlands – May 1940 Prime Minister May 10, 1940 France Threatened France & the Maginot Line French Defense Maginot Line Static Defense Hinges on Luxembourg & Belgium Fort Eban Emael – Belgium French Invasion May 10 – May 22, 1940 Advance through Ardennes Bypass Maginot Line British Expeditionary Force Maginot Line Rescue at Dunkirk May 26 - June 3, 1940 Operation Dynamo British and French Forces Halt of German Panzers Role of Luftwaffe Rescue of Allied Forces 200,000 British troops 140,000 French troops Great Britain Last European Democracy Dunkirk "We must be very careful not to assign to this deliverance the attributes of a victory. Wars are not won by evacuations.“ Winston Churchill France Defeated Occupied France Occupied France Vichy France Marshall Petain Collaboration French Navy French Resistance Free French Eventually 400,000 General De Gaulle De Gaulle and Petain The German Reich: 1940 The Battle of Britain July 10 – Oct. 31, 1940 Prelude to Russia Operation Sea Lion Planned Invasion of Great Britain Sea-based Invasion Control of English Channel Airpower Luftwaffe & RAF Air Supremacy Battle of Britain Battle for Air Supremacy Luftwaffe Over Great Britain Over English Channel Herman Goering Air Attacks & Bombing The “Blitz” – Cities Great Britain Role of RADAR Role of RAF Retaining Pilots Battle of Britain “Never in the field of human conflict was so much owed by so many to so few.” Winston Churchill The “Blitz” 60,000 Killed 87,000 Injured 2 Million Homes Destroyed America’s Response Disarmament after WWI Depression Avoidance of European Conflicts Opposition to Germany 1939 – 18th in Military Power Fascism Anti-Semitism German Aggression Awe at Germany Charles Lindbergh Joseph Kennedy “The Arsenal of Democracy” Roosevelt Administration “Cash and Carry” 1939 50 Destroyers Election of 1940 99-Year Naval Leases Roosevelt vs. Willkie Isolationist Campaign Lend-Lease Act - 1941 7 Billion in Weapons & Supplies Extension to Soviet Union Barbarossa: Sept. 22, 1941 Battle of the Atlantic German Strategy Initial Success Cut off British Supplies Attack All Shipping “Wolfpacks” 200 Ships Sunk – June 1940 Allied Strategies Convoy System “Escorts” Intelligence Ship Production Battle of the Atlantic Allied Cost of Battle 30,000 Merchant Seamen 2,200 Merchant Ships 100 Allied Naval Vessels Over 600 Allied Aircraft 3 Million Tons of Shipping German Cost of Battle 510 U-Boats (2/3rds) 18,000 U-Boat Men U-505 The Atlantic Charter August 1941 American Neutrality Newfoundland War Aims Churchill Roosevelt Self-Determination Peace Europe First Strategy Japanese in the Pacific Japanese Expansion Natural Resources Nationalism “Greater East Asia CoProsperity Sphere” Tripartite Pact China and Manchuria September 26, 1940 Germany, Japan, Italy Axis Nations Role of Military Role or Emperor America and Japan Japanese Seizure of French Indochina American Response Free Japanese Assets Block Sale of Oil and Iron Demand Evacuation of China and Indochina Japanese Response U.S. as Threat in Pacific Diplomacy Eliminate U.S. Pacific Fleet Pearl Harbor: Dec. 7, 1941 Failed Negotiations No Declaration of War Admiral Yamamoto’s Plan Surprise Attack Shallow Running Torpedoes Midget Submarines Destroy Pacific Fleet Give Japan Time Break American Will Attack on the Philippines Pearl Harbor: Dec. 7, 1941 Pearl Harbor: Dec. 7, 1941 Pearl Harbor: Dec. 7, 1941 Pearl Harbor: Results U.S. Losses U.S. Reaction 18 Ships Sunk or Damaged 170 Aircraft Destroyed 3,700 Casualties Panic on East Coast Anger Declaration of War December 8, 1941 “Will live in infamy” Japanese Expansion December 8, 1941 December 10 Wake Island Landing December 12 Guam Attacked December 11 Philippines Attacked Luzon Landing December 13 Hong Kong Fall of the Philippines 22,000 American Troops Lack of Supplies Fighting Retreat to Corregidor Recall of Gen. McArthur March 1942 “I shall return” U.S. Surrender April 10, 1942 General Wainwright 11,000 U.S. Troops Bataan Death March Bushido Geneva Convention Over 600 Deaths 70,000 Prisoners 10,000 Deaths Camp O’Donnel Cabanatuan America’s Response Striking Back at Japan American Morale Logistical Problems Doolittle's Raiders 80 Men 16 B-25 Bombers Losses Morale Boost Doolittle Raid: April, 1942 The Home Front Mobilization 1940 Selective Training & Service Act 1st Peacetime Draft 21-35 18-45 15 Million Americans Serve Segregation Wartime Economy Manufacturing Arsenal of Democracy Factory Jobs – Pay North & Midwest War Production Board Office of War Mobilization Citizens Scrap Drives Rationing Office of War Information Taxes – Middle & Lower Classes War Bonds The War in Europe & Africa A Desperate Situation Late 1941 Battle of the Atlantic Nazi Advances: Post Pearl Harbor Churchill & Roosevelt Reaffirm Atlantic Charter Greece Yugoslavia Soviet Union North Africa Germany 1st Soviet Union & China Join Allies in 1942 Soviet Union and China Taking the War to Germany 1942 Battle of the Atlantic Long-Range Bombing Ground Offensive Night – RAF – Cities Day – AAF – Factories Soviet Needs Allied Plans Where & When? France North Africa • 3.4 Million Tons of Bombs • 12,000 Heavy Bombers Lost • Over 100,000 Killed The Memphis Belle North Africa The Suez Canal Sept. 1940 Italian forces attack Egypt British counter German Reinforcement Afrika Corps General Erwin Rommel “The Desert Fox” Battle of El Alamein Operation TORCH General Montgomery “Desert Rats” Nov. 8, 1942 Afrika Corps Defeated - 1943 TORCH – Nov., 1942 HUSKY – July, 1943 Invasion of Sicily “Soft Underbelly of Europe” “Friendly” Losses General George Patton Invasion of Italy September, 1943 Italian Surrender German Reaction Rescue of Mussolini German Occupation Anzio – January, 1944 D-Day: Operation Overlord June 6, 1944 Allied Invasion of Europe Gen. Dwight D. Eisenhower Supreme Allied Commander 23,000 Paratroopers 130,000 Landing Troops 195,000 Naval Support 2,000,000 Total Invasion Force 9000 Casualties – 3000 KIA Battle of the Bulge December 16, 1944 25 German Divisions “Last Ditch” Effort German Push to the Coast 77,000 American Casualties Bastogne 101st Airborne General McAullife “Nuts” Battle of the Bulge VE Day May 8, 1945 Dresden, Feb. 1945 Operation Varsity Berlin America or Soviet Union Soviet Advance to Berlin Surrender Crossing the Rhine Hitler’s Suicide The Holocaust Rebuilding The “Cold War” The Holocaust The Holocaust The Holocaust The Pacific Theater Fighting in the Pacific Admiral Chester Nimitz Commander of U.S. Navy General Douglas McArthur Command of Troops Breaking Japanese Code Battle of the Coral Sea Loss of USS Lexington Battle of Midway June 3-6, 1943 4 Japanese Carriers Lost Island-Hopping Strategy Islands Guadalcanal New Guinea Gilbert Mariana Marshall Air Fields – Bombing Submarines Advance in the Pacific Battle of Leyte Gulf Island-Hopping October 1944 Philippines McArthur’s Return Okinawa Saipan Iwo Jima Kamikazes Manhattan Project Roosevelt’s Death Franklin D. Roosevelt Elected to Four Terms 1933-1945 Vice-President Last Days Harry S. Truman Yalta Conference – Feb. 1945 April 12, 1945 Warm Springs, Arkansas President Truman Hiroshima & Nagasaki VJ Day August 15, 1945