* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovasular-Heart-2404heart02-22-07
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
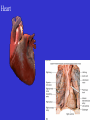
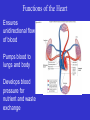
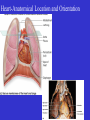
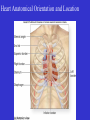
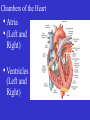
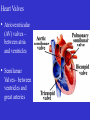
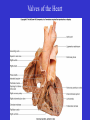
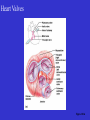
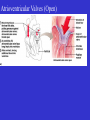
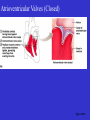
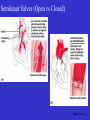
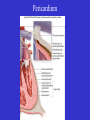
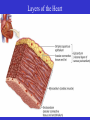
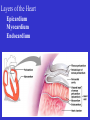
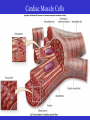
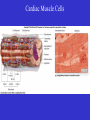
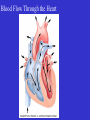
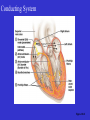
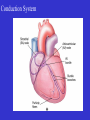
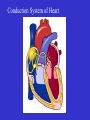
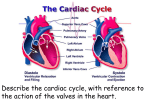
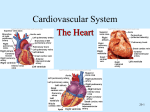
Heart Figure 22.02b Heart Functions of the Heart Ensures unidirectional flow of blood Pumps blood to lungs and body Develops blood pressure for nutrient and waste exchange Figure 22.01 Heart-Anatomical Location and Orientation Heart Anatomical Orientation and Location Chambers of the Heart • Atria • (Left and Right) • Ventricles (Left and Right) Heart Valves • Atrioventricular (AV) valves – between atria and ventricles • Semilumar Valves– between ventricles and great arteries Valves of the Heart Heart Valves Figure 18.8a Atrioventricular Valves (Open) Atrioventricular Valves (Closed) Figure 18.9b Semilunar Valves (Open vs Closed) Figure 18.10a, b Pericardium Layers of the Heart Layers of the Heart Epicardium Myocardium Endocardium Figure 18.3 Cardiac Muscle Cells Cardiac Muscle Cells Blood Flow Through the Heart Figure 22.06ab Conduction System • Cardiac muscle tissue has intrinsic ability to: • Generate and conduct impulses • Signal these cells to contract rhythmically • Conducting system • A series of specialized cardiac muscle cells • Sinoatrial (SA) node sets the inherent rate of contraction Conducting System Figure 18.12 Conduction System Conduction System and ECGs Conduction System of Heart Disorders of the Heart • Coronary artery disease • Atherosclerosis – fatty deposits • Angina pectoris – chest pain • Myocardial infarction – blocked coronary artery • Silent ischemia – no pain or warning Disorders of the Heart • Heart failure • Progressive weakening of the heart • Cannot meet the body’s demands for oxygenated blood • Congestive heart failure – heart enlarges • Pumping efficiency declines • Cor pulmonale • Enlargement and potential failure of the right ventricle Disorders of Conduction • Ventricular fibrillation • Rapid, random firing of electrical impulses in the ventricles • Atrial fibrillation • Multiple waves of impulses randomly signal the AV node • Signals ventricles to contract quickly and irregularly