* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download “Put that in the Form of a Question, Please!”
Survey
Document related concepts
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
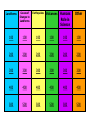
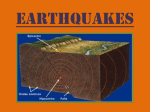
Chapter 2 Review Constructive & Destructive Forces Landforms Causes of Changes to Landforms Earthquakes Volcanoes Humans Role in Science Other 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Which landform is much higher than the surrounding land? Mountain What is a sand dune? A sand hill that is made and shaped by wind What is a plain? A large, flat landform with little relief What does the word “mesa” mean in Spanish? table Name 2 Mountain Ranges. Rocky Mountains Appalachian Mountains What is the process of wearing away rocks? weathering What is erosion? The process of moving sediment by wind, water, or ice What is deposition? The process by which sediment drops out of water Where would you most likely find a delta? Near a river’s mouth Give 2 examples of weathering. 1. Waves crashing against a cliff 2. a plant growing in a crack in a rock 3. sand blowing against a rocky surface Name the 4 earth’s layers. Crust mantle outer core inner core What is an earthquake? Movement of the ground caused by a sudden release of energy in Earth’s crust What is a fault? A break in Earth’s crust Who is a seismologist? A person who studies earthquakes What causes an earthquake? A sudden release of energy in Earth’s crust What is a volcano? A mountain made of lava, ash, or other materials from eruptions What is magma? Melted, molten rock that is beneath Earth’s surface What causes a chain of volcanoes to occur? The movement of a plate over a hot spot What is a column of hot magma called? A hot spot What group of islands was formed by a chain of volcanoes? Hawaiian Islands What is a wall-like structure that sticks out into the ocean? A jetty Name 1 method of flood control. Dam, levee, or allowing rivers to reclaim floodplains What does a seismograph record? Movements in Earth’s crust What does the root word “seismos” mean? Shock or earthquake How do seismologists help prevent earthquake damage? They locate areas most likely to shake during quakes, and allow people to plan safety programs. How can earthquakes be destructive? Roads and bridges are damaged, buildings fall Where does the most damage usually occur from an earthquake? An epicenter How do mountains form? Where plates come together, part of the crust is forced up. When pressure is applied, the edges of a plate may be forced up. Which layer of the Earth’s crust contains soft areas on which plates float? mantle What causes a sinkhole to form? Water weathers and erodes soft rock underground, forming a cave. If the roof of the cave collapses and the cave is near the surface, a sinkhole forms.