* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heat - Warren County Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Insulated glazing wikipedia , lookup
Thermal comfort wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic insulation wikipedia , lookup
Space Shuttle thermal protection system wikipedia , lookup
Passive solar building design wikipedia , lookup
Underfloor heating wikipedia , lookup
Thermal conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Thermoregulation wikipedia , lookup
Intercooler wikipedia , lookup
Solar water heating wikipedia , lookup
Heat exchanger wikipedia , lookup
Building insulation materials wikipedia , lookup
Solar air conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Heat equation wikipedia , lookup
Cogeneration wikipedia , lookup
Copper in heat exchangers wikipedia , lookup
R-value (insulation) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
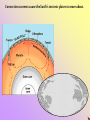
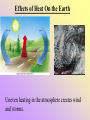
HEAT AND HEAT TRANSFER What is the difference between temperature and heat? Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of atoms. Thermometers are used to measure temperature This means: the higher the temperature, the faster the atoms move the lower the temperature, the slower the atoms move Less Heat More Heat If energy is added to atoms, they move faster. The faster they move, the further apart they move. This spreading out of atoms happens in solids, liquids and gases. The term for this type of expansion is called THERMAL EXPANSION. Thermal expansion is why running a tight jar lid under water loosens the lid. Read pgs. In the textbook to see other examples of thermal expansion. WHAT IS HEAT? The ancients used to think that heat was an invisible, weightless fluid that flowed from hot things to cold things. ACTUALLY Heat is transfer of energy between objects of different temperatures caused by atoms rubbing together How cold is cold? There is no such thing as coldness. What we call cold is really absence of heat or slow atoms. Even when it is 15 degrees outside, that is 15 degrees of HEAT, NOT 15 degrees of COLD. Another word for heat is THERMAL ENERGY. Heat (thermal energy) is transferred from warmer objects to cooler objects Can a balanced temperature ever be reached? YES, IT’S CALLED THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM No energy transfer occurs HEAT IS TRANSFERRED IN THREE WAYS BY CONDUCTION CONVECTION RADIATION CONDUCTION Transfer of heat from one substance to another by direct contact of molecules. Happens in solids, liquids and gases Best conduction happens in solids Examples: Sauce pan on a stove top, metal spoon in a bowl of soup, ice melting in a warm hand, hot shower, walking on hot coals Objects that heat up easily are called CONDUCTORS. Metals are the best conductors Metal objects feel cold because they conduct heat AWAY from your hand Objects that DO NOT heat up easily are called INSULATORS. Things like glass,wood, plastic and rubber are good insulators Which parts of the pan are conductors and which are insulators? CONVECTION Transfer of heat in liquids and gases ONLY Heat moves up and down in a motion called a CONVECTION CURRENT Heated liquids and gases are less dense & rise carrying heat with them Examples: movement of plate, ocean currents, home furnace heating & circulating air Convection Currents in The house Convection Current Convection currents cause the Earth’s tectonic plates to move about. RADIATION transfer of heat through empty space in form of infrared radiation waves (what we think of as heat waves) When light strikes an opague object, it converts into heat Examples: blacktop heats up on a sunny day, hot sand on a beach, electric heaters. Explain how each of these uses radiant heat. How does heat affect matter? Physically: heat changes the state in which matter exists i.e. melting, freezing, evaporating, condensing Chemically: for chemical reactions to occur, chemical bonds must be broken and new compounds formed. Requires energy to be absorbed or released Effects of Heat on the Earth Large bodies of water moderate the climate. The temperatures are not as extreme!! Ocean CurrentsCaused by convection Currents. Effects of Heat On the Earth Uneven heating in the atmosphere creates wind and storms.