* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Soft Tissue Infections
Survey
Document related concepts
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
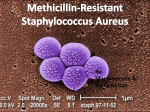
Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
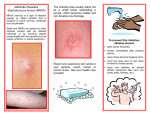
Soft Tissue Infections Lawrence L. Lambert Off Shore Paramedic Acadian Integrated Services Staphylococcus Aureus • Commonly called staph • Bacteria commonly found on human skin • Commonly found – Inside the nose – Armpit – Groin – Genital Areas MRSA Methicillin-resistant S. Aureus • Symptoms – Reddness – Warmth – Swelling – Tenderness – Boils or blisters – Often mistaken for spider bites – Fever and chills How is MRSA Spread? • Close contact with infected persons • Staph can come off skin during skin to to skin • • contact Staph can come off the skin onto shared objects and surfaces and can get into the skin of another person who uses that object or surface Through the drainage and pus which is very infectious Who is at risk for MRSA Infections? • Those with recurrent skin diseases or open wounds • Long term illness • Been a patient at a hospital or other health care facility within the past year Who is at risk for MRSA Infections? • Contact with persons with MRSA infections • Recent Antibiotic use • Live in crowded settings MRSA is diagnosed through a culture being taken and sent to the laboratory How is MRSA treated? • Proper wound and skin care using antibiotics • Incision and drainage (I&D) • More serious infections may require IV antibiotic treatments How can I protect myself from becoming infected with staph • Keep your hands clean by washing thoroughly with soap and water • Keep cuts and abrasions clean and covered with a clean bandage until healed How can I protect myself from becoming infected with staph • Avoid contact with other employee wounds • Clean objects and surfaces that are shared with other employees before you use them If I have MRSA or staph how can I keep from spreading it? • Keep infections covered with clean, dry bandages • Wash hands after touching exposed skin and bandages • Do not share personal items • Keep your clothes clean • Avoid skin to skin contact with others What should I do if I think I have a staph infection? • Consult your medic immediately • Early treatment can help prevent the infection from getting worse • Control the spread!!!