* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MRSA Frequently Asked Questions
Survey
Document related concepts
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
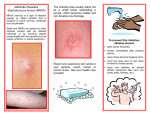
MRSA Frequently Asked Questions What is Staphylococcus aureus (staph)? Staphylococcus aureus, referred to commonly as "staph" are bacteria commonly carried on the skin or in the nose of healthy people. Approximately 30%-50% of the population is colonized (when bacteria are present, but not causing an infection) in the nose with staph bacteria. Sometimes, staph can cause skin infection. Historically, staph infections occurred among persons in hospitals and healthcare facilities but now they are rapidly spreading into the general population and are easily spread from person to person. What is MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus)? What is community-acquired MRSA or CA-MRSA? What does a staph or MRSA infection look like? Staph bacteria, including MRSA, can cause skin infections that may look like a pimple, boil or ingrown hair and can be red, swollen, painful, or have pus and other drainage. Many occur in the armpits, neck, groin and buttocks where bacteria grow. More serious infections may cause pneumonia, bloodstream infections, or even death. How is MRSA spread? How can I prevent staph or MRSA skin infections? Practice good hygiene including: Keep your hands clean Treat cuts and scrapes with StaphAseptic® First Aid Antiseptic/Pain Relieving Gel (not triple antibiotic!) Keep cuts and scrapes clean and covered with a bandage until healed Shower after physical activity Properly clean gear and equipment Consult your trainer/physician for all active wounds Avoid contact with other people's wounds or bandages Avoid sharing personal items such as towels or razors