* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 13-DNA Technology
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Mycoplasma laboratorium wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
History of biotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Gene prediction wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
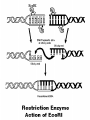
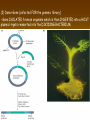
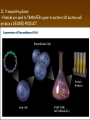
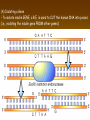
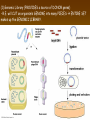
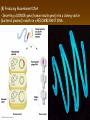
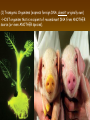
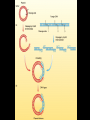
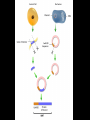
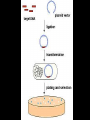
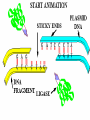
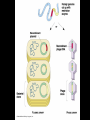
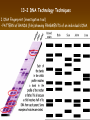
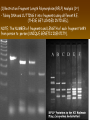
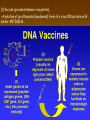
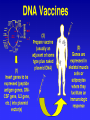
Chapter 13: DNA Technology 13-1 The New Genetics 13-2 DNA Technology Techniques 13-3 Practical Uses of DNA Technology 13-1 Chromosomes and Inheritance I. Manipulating Genes (base sequences) • Genes must be IDENTIFIED and ISOLATED before INSERTED from one cell type to another. Critical Thinking (1) List three ways that genetic engineering could be used to improve the lives of humans. (1) DNA Technology (modern application, Genetic Engineering) • Use of “restriction ENZYMES” and “cloning VECTORS” to change the ACTIVITY of genes (and thus cells). Critical Thinking (2) What are some common genetic disorders that afflict the human population that may be treatable with DNA biotechnology? (A) Restriction Enzyme (isolated from bacteria cells) • Cuts DNA into SMALLER pieces at specific SEQUENCES of bases. (Ex: EcoRI recognizes CTTAAG and GAATTC cuts between A -G bases) (1) Sticky Ends (complementary base-pairs MUST match to bond) • SINGLE chain “TAILS” RESULT when DNA is CUT by enzymes at specific restriction sites. (B) Cloning Vectors (i.e., recombinant plasmids) • Carriers used to TRANSFER foreign DNA from one organism TO another. (1) Plasmid (accepts foreign DNA) • RING of bacterial DNA that is ISOLATED and CUT so a DONOR GENE can be inserted. (2) Donor Gene (collected FOR the genomic library) • Gene ISOLATED from an organism which is then INSERTED into a HOST plasmid gets reinserted into the DIVIDING BACTERIUM. (3) Gene Clone • As BACTERIAL CELL divides, copies of DONOR GENE are made and PLASMIDS containing these GENE CLONES can be COLLECTED. II. Transplanting Genes • Plasmids are used to TRANSFER a gene to bacteria SO bacteria will produce a DESIRED PRODUCT. (1) Insulin • Protein that MOVES glucose INTO cells; (Bacteria are engineered to manufacture MASS quantities of human insulin for DIABETICS). (A) Isolating a Gene • To isolate insulin GENE, a R.E. is used to CUT the human DNA into pieces (i.e., isolating the insulin gene FROM other genes). (1) Genomic Library (PROVIDES a source of DONOR genes) • R.E. will CUT an organism’s GENOME into many PIECES ENTIRE SET makes up the GENOMIC LIBRARY. (B) Producing Recombinant DNA • Inserting a DONOR gene (human insulin gene) into a cloning vector (bacterial plasmid) results in a RECOMBINANT DNA. (1) Recombinant DNA (two or more sources) • Processed DNA combination from DONOR and HOST source. (C) Cloning DNA • Recombinant plasmid is COPIED many times, making CLONES of the GENE for INSULIN. (1) Transgenic Organisms (express foreign DNA, doesn’t originally own) • HOST organism that is recipient of recombinant DNA from ANOTHER source (or even ANOTHER species). Critical Thinking (3) The FDA does not require special labels for genetically engineered food products that are identical to similar products produced by traditional breeding techniques. Do you think that genetically engineered food products should be labeled as such? Why or why not? III. Expression of Cloned Genes (challenges have led to TWO techniques) (1) To INDUCE a bacterial host cell to express a FOREIGN gene involves the additional transfer of PROMOTERS that turn on the DONOR gene. (2) The DONOR gene is inserted NEXT to a gene that is normally produced in LARGE quantities within the cell. (i.e., the donor gene is expressed ALONG WITH the host cell’s frequently expressed gene). 13-2 DNA Technology Techniques I. DNA Fingerprint (investigative tool) • PATTERN of BANDS (film) showing FRAGMENTS of an individual’s DNA. (A) Making a DNA Fingerprint A FOUR-Step Process (1) DNA sample is CUT into many fragments by R.E. (2) DNA fragments are SEPARATED by gel electrophoresis. (3) Radioactive probes ADDED will bind to select DNA fragments. (4) Photographic FILM allows visualization resulting in a DNA fingerprint. (1) Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) Analysis (1st) • Taking DNA and CUTTING it into fragments using different R.E. (THESE GET LOADED INTO GEL). NOTE: The NUMBER of fragments and LENGTH of each fragment VARY from person to person (UNIQUE GENETIC IDENTITY). (2) Gel Electrophoresis (2nd fragments MOVE through a GEL) • SEPARATES fragments BY SIZE (smaller = further DOWN) using LANES and 2 opposite (+/-). NOTE: DNA fragments (-) MOVE towards the POSITIVE (+) end & DISTANCE traveled is dependent on the SIZE. (3) Radioactive Probes (3rd Selected probes added to DNA AFTER gel ) • Bind to DNA, forming BANDS when exposed to photographic FILM. (RESULTS in DNA fingerprint) NOTE: The DNA fragments on the gel are BLOTTED onto FILTER PAPER once they are done running (TO PRESERVE THE PATTERN). (B) Accuracy of DNA Fingerprints (MORE variability MORE accuracy) • MOST ACCURATE NONCODING regions where DNA REPEATS OVER AND OVER; found in individual’s genome (called HYPERVARIABLE regions) NOTE STATISTIC: DNA fingerprint compares the HV patterns at FIVE different SITES, and it is HIGHLY unlikely (1 in a million) that ALL five sites compared will MATCH EXACTLY between TWO people. (C) Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR allows you to make a DNA fingerprint ) • PCR used to turn a SMALL sample into THOUSANDS of copies of DNA (i.e., the MORE DNA available, the BETTER the fingerprint). • In order to RUN PCR, you must have a SUPPLY of… (1) Original DNA sample (trace amount) (2) DNA Polymerase (DNA Builders) (3) Primers (DNA Starters) (4) DNA Nucleotides (A, T, C, G) (1) Primer (STARTS replication of trace DNA) • A single-stranded DNA required for INITIATION of DNA replication during PCR. II. Human Genome Project (46 countries, 1990-2003) 2 shared GOALS have been SET… (1) To figure out the BASE SEQUENCE of entire human genome (approximately 3 billion base pairs—100,000 genes) (2) To map (identify AND isolate) the location of GENES on each of our 46 chromosomes. The BENEFITS of learning our GENOME may include… (1) Improving diagnoses, treatments, and CURES for ~ 4,000 GENETIC disorders. (2) Improving our understanding of HOW genomes are organized in OTHER species, including how EVOLUTION may occur. (A) Gene Therapy (early 1990’s experimental treatment) • Introducing (through a vector) a HEALTHLY GENE into a cell OR by CORRECTING a gene defect in a cell’s genome. EX: Nasal sprays (w/ NORMAL cystic fibrosis gene) are INHALED into nose and lungs, where there are cells affected by diseased c.f. genes. (B) Ethical Issues (Bio-Ethics) • Where should POLICY draw line of REPAIRING genes versus REMODELIN human genes? (i.e., Designer genes? Who can AFFORD treatments?) NOTE: Opponents worry this KNOWLEDGE of our genome could lead to a new form of discrimination called… Genoism 13-3 Practical Uses of DNA Technology I. Producing Pharmaceutical Products (i.e., medicines) • To engineer BACTERIA to make human PROTEINS (i.e., insulin). Examples include… (1) Human Growth Hormone (HGH) as a treatment for DWARFISM. (2) Interferon Treat viral infections by PREVENTING replication. (3) Tissue Plasminogen Activator (TPA) to dissolve blood clots (strokes). (A) Genetically Engineered Vaccines (contain DNA from PATHOGENS) • Genes coding for ANTIGENS are INSERTED into a HARMLESS VIRUS. • GOAL: Imitate the REAL virus’s ANTIGENS, so that human IMMUNE system can be prepared to defend (i.e., mock viruses). (1) Vaccine (provides immuno-recognition) • A solution of an attenuated (weakened) form of a virus OR bacteria with similar ANTIGENS. (2) Pathogen (antigens OUTSIDE) • Disease-causing AGENT that is TREATED to become a VACCINE. II. Increasing Agricultural Yields (Herbicides and Pesticide Alternatives) • New plants pest/disease resistant, larger fruit, more nutritious, stay ripe longer; altering plant genome (Ex: Tomato Enzyme—Hornworm) (1) Herbicides (herbicide resistant CROPS wheat, cotton, and soybeans) • Chemicals designed to kill WEEDS can ALSO disrupt CROP GROWTH. (A) Crops That Do Not Need Fertilizer (using BACTERIAL genes) • Transgenic plants can “FIX” N2 out of ATMOSPHERE instead of obtaining it through EXPENSIVE fertilizer. Critical Thinking (4) The United States government has stringent regulations requiring researchers to confine genetically engineered organisms to the laboratory. What concerns do you think might have led to the enactment of these regulations? III. Safety & Environmental Issues (i.e., Regulating Genetic Engineering) • Standards are set for SALE of genetically engineered FOOD products (Health risks (NEW allergies) AND ecological risks SUPERWEEDS). (1) Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (2) National Institutes of Heath Recombinant DNA Advisory Committee (3) Department of Agriculture (USDA) (4) Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (A) Genetically Engineered Foods • Long-term effects of CONSUMPTION = UNKNOWN NEW food allergies and toxins arising unexpectedly. Critical Thinking (5) Natural selection is a mechanism of evolution whereby the members of a population who are best adapted to their environment survive and produce offspring. How might natural selection become affected by genetic engineering? (B) Genetically Engineered Crops (pest-resistant, herbicide-resistant) • Concern THESE crops could SPREAD into WILD and wipe out NATIVE plant species (ECOLOGICAL damage to food chains).