* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
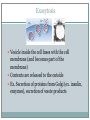
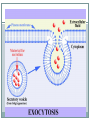
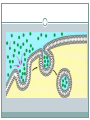
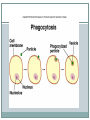
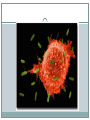
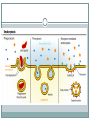
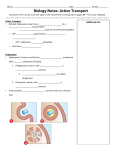
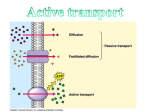
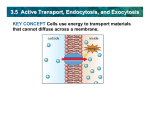
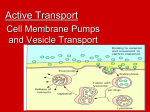
TRANSPORT ACROSS CELL MEMBRANES Endocytosis and Exocytosis Learning Outcomes B9 - Describe the structure and function of the cell membrane: Describe and compare endocytosis and exocytosis in terms of: Method of transport (use of vesicles) Use of energy (active vs. passive) Type / size of molecule transported Enodcytosis and Exocytosis Exocytosis and Endocytosis vesicles move substances in and out of cells vesicles can fuse with the cell membrane (where might they be coming from?) new vesicles or vacuoles can be formed from the cell membrane Active (requires ATP for energy) Exocytosis Vesicle inside the cell fuses with the cell membrane (and becomes part of the membrane) Contents are released to the outside Ex. Secretion of proteins from Golgi (ex. insulin, enzymes), secretion of waste products Endocytosis Takes substances into the cell Plasma membrane forms a vesicle around a substance and takes it in (Note that part of the plasma membrane becomes the vacuole) Pinocytosis (“cell drinking”) - liquid or small particles taken in by tiny vesicles Phagocytosis (“cell eating”) – entire cells or large food particles are taken in - ex. white blood cells take in bacterial cells, which are then destroyed by lysosomes White blood cell phagocytizing bacteria Receptor Mediated Endocytosis the particle being taken in first binds to a specific receptor protein on the outside of the cell membrane Organelles and Membrane Working Together