* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vectors for Even Larger Genomic DNA Inserts
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
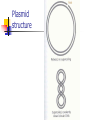
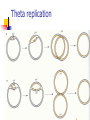
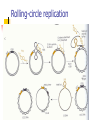
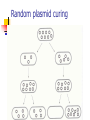
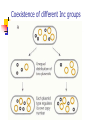
Microbial Genetics (Micr340) Lecture 7 Plasmids Plasmids DNA molecules other than chromosomes Widely present in most bacteria Roles: adaptation, evolution, pathogenesis Usually encode genes not essential Mostly circular Sizes: a few kb to >100 kb Naming Plasmids Many name after genes they carry or functions of the plasmids In the beginning: ColE1, producing Bacteriocin to kill E. coli Tol, degradation of toluene Ti, Tumor initiation in plants RK2, resistance to amp, tet, kanamycin Now: pXXNNNN. eg, pHX200 Plasmid structure Plasmid purification Plasmid purification Plasmid replication Replicons: DNA molecules that can replicate autonomously in cell (chromosome, plasmid) All replicons have at least one origin of replication (ori) For plasmid ori, it is called oriV (vegetative) Two mechanisms of replication: Theta replication Rolling-circle replication Theta replication Rolling-circle replication Function of ori region Replication related genes close to ori. Host range determination Narrow host range Broad host range Regulation of copy-number Relaxed plasmids – high copy-number Stringent plasmids – low copy-number Regulation of replication: ColE1 plasmids Random plasmid curing Plasmid Partition Plasmid avoid being lost from dividing cells by carrying partitioning systems The functions involved in these systems are called par functions cis-acting site: parS trans-acting site: parA and parB Incompatibility Many bacteria contain multiple types of plasmids and can coexist for many generations Not all types of plasmids can stably coexist in same cell; some interfere with each other’s replication or partition and one of them will be lost This is called plasmid incompatibility Incompatibility Two plasmids that cannot stably coexist are members of the same incompatibility (Inc) group If two plasmids can stably coexist, they belong to different Inc group Coexistence of different Inc groups Coexistence of same Inc groups Measuring curing of a plasmid Finding the ori of a plasmid