* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Macroevolution
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
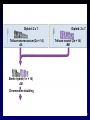
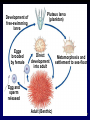
Evolution of Genomes and Developmental Mechanisms Chapter 24 1 Comparative Genomics • Chimpanzee – Humans and chimps diverged from a common ancestor about 5 mya. share about 98.7% of genes 2 Origins of Genomic Differences • Genome changes arise in at least six ways. – mutation of a single gene – regions of DNA duplicate – large chunks of chromosomes rearrange – individual chromosomes duplicate – whole genomes duplicate or combine to create polyploids – integration of foreign DNA 3 Polyploidization • There is growing evidence that duplication of fewer genes in organisms has been a major contributor to morphological diversity. – Polyploidy can result from either genome duplication in one species or from hybridization of two different species. 4 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Haploid Diploid Polyploid 5 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Diploid: 2 x 7 Triticum monococcum (2n = 14) AA Diploid: 2 x 7 Triticum searsii (2n = 14) BB Sterile hybrid (1n = 14) AB Chromosome doubling 6 Lateral Gene Transfer • Phylogenies are built on the assumption that genes are passed from generation to generation (vertical gene transfer). – Hitchhiking genes from other species lead to phylogenetic complexity referred to as lateral gene transfer. 7 Evolution of Development • Genes with similar sequences in two different species may work in different ways. – regulatory gene may turn on different sets of genes in different organisms – changing time of gene expression can also result in dramatic changes in shape – Convergent function recruitment of existing regulatory programs for new functions 8 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Development of free-swimming larva Eggs brooded by female Pluteus larva (plankton) Direct development into adult Metamorphosis and settlement to sea-floor Egg and sperm released Adult (Benthic) 9