* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Power Point 2 - G. Holmes Braddock
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
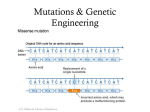
SC.912.L.16.3 SOEL OCANA PERIOD.5 DNA replication ? DNA replication- the basis for biological inheritance, is a fundamental process occurring in all living organisms to copy their DNA. The basis for biological inheritance is basically when DNA makes copies of itself DNA replicate is the copying of a double stranded DNA molecule producing two identical DNA double helices. You can think of DNA replication as a zipper on a sweater it divides into two strands unwinding itself when zipped down, then winding itself back up forming a “DNA molecule” Gene & Chromosomal mutations Genes – factor that is based on from parents to the offspring. Chromosomal mutation – an alteration to the chromosome . Genes are basically a code in our DNA everyone has genes, families most often may share a lot of the same genes. When there is a mutation in a chromosome there is most probably something wrong with the species. Chromosomal mutations can sometimes be genetic. Some examples of chromosomal mutations are …. a) Down Syndrome b) Color Blindness Phenotypic Change Phenotype – physical characteristic of an organism A phenotypic change is a change in an organisms appearance A mutation may result in a phenotypic change if the mutation occurs at a point on the gene that determines the phenotype. Mutations don’t always result in phenotypic change. Phenotypic change is mostly seen when looking into evolution Evolution is the change of a species over time Transcription- synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template The process of transcription is basically when the enzymes copy DNA to produce the proper RNA to run the organism. This process creates proteins which make life possible. Viruses like HIV and AIDS have the ability to read the cell’s transcription, which help the virus keep making copies of itself. That is why it is so hard and nearly impossible to ever get rid of HIV. Genetic Code Genetic Code – collection of condos of mRNA. Is the genetic code most common in almost all organisms ? Yes, the genetic code is common. Why ? Well because all organisms we know on earth today evolved from a common ancestor which used this same genetic code. Similarities in Genetic Code Similarity in genetic code are due to common ancestry because way back when we all shared a common gene with one of our ancestors and that is why we all have a similar genetic code. Process Of Inheritances Biological Inheritance – the process in which a living organism produces another organism that shares its same traits. Inheritance results in specific variations and is the cornerstone for evolution. Evolution is mostly based on characteristics and physical traits that have been passed down for generation to generation