* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inheritance - Glen Rose FFA
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
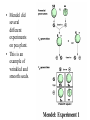
Inheritance Chapter 7 Inheritance: the way genes are passed down. • If a father doesn’t have a leg does that mean his children will be born with out a leg???? Hundreds of years ago people knew that somehow certain traits would be passed on to their children. Gregor Mendel was the first to predict the outcome of inheritance. The study of inheritance is Genetics. • Mendel did several different experiments on pea plant. • This is an example of wrinkled and smooth seeds. Genes and Alleles • A gene is a specific piece of DNA. • You have two genes that code for the same thing (ex. Height). Each of those two genes is called an allele. • So if something had the genes Aa one allele would be “A” the other would be “a”). Why two alleles for every gene? • Because organisms get 2 sets of chromosomes ……….one from the mother and one from the father. Phenotype • Is the physical characteristics of the trait. • In most cases it is what we can “see”. • Example: Freckles, dimples, attached earlobes etc. Genotype • Is the actual alleles that make up the trait. • In most all cases this is represented by 2 letters. • Example: AA, Aa, aa Dominant – A dominant trait is a trait that covers or hides the other trait of an allele. • For example, dark colors in hair usually overshadow the other allele. • In this class Dominant will always be represented with a capital letter. • Example: Say “D” is the allele for black hair and “d” is the allele for blond. The if an animal had Dd then it would have black hair. Recessive • A recessive trait is the trait that is hidden by the dominant trait. • In an animal with Dd for hair color the recessive allele is “d”. • The animal carries a gene for blond hair but you can’t tell by looking at it. Heterozygous • This is the term given two different alleles. • For example, Aa is heterozygous. • It may contain one gene for brown eyes(A) from the mother and one gene for blue(a) eyes from the father. Homozygous • This is the term given to the two same alleles. • For example, AA or aa • A person may contain 2 genes for -brown eyes – one from each parent (AA) or 2 for blue (aa).