* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
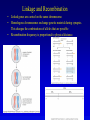
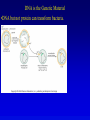
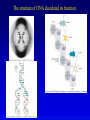
Chapters 1-2 Mendelian Genetics and Nucleic Acid Structure 23 August, 2006 Overview • Mendel refuted the blending hypothesis, proposing particulate units of inheritance - genes. • The idea of genetic inheritance gained support from the behavior of chromosomes in meiosis and fertilization. • Linkage analysis can give information about the relative location of genes on chromosomes. • The success of Mendelian genetics increased the importance of characterizing the genetic material. • Chromosomes are composed of DNA and protein - the DNA is the genetic material. • Nucleic acid structure gives important insight into genetic function. Review of Mendelian Inheritance • Genes influence characters, and may occur in a number of different allelic forms. •Each organism / cell has two copies of each gene, and may be homozygous or heterozygous. •Gametes carry a single allele of each gene. Alleles are distributed randomly to gametes. •Fertilization combines the alleles present in the two participating gametes. Incomplete Dominance Independent Assortment Linkage and Recombination • Linked genes are carried on the same chromosome. • Homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material during synapsis. This changes the combinations of alleles that are possible • Recombination frequency is proportional to physical distance. Genetic maps use crossover frequency to order groups of linked genes. •Genes are carried on chromosomes, and are inherited unchanged and undiluted. •Mutations are rare events that change one allele to another. •A genetic material that was inherited unchanged and undiluted, but subject to rare mutation answered a major flaw in evolutionary theory. •The success of genetics intensified interest in the nature of the genetic material. •Chromosomes are composed of DNA and Protein. Most biologists thought that Protein was the genetic material, while DNA was structural. DNA is the Genetic Material •DNA but not protein can transform bacteria. Viral Genes are nucleic acids The structure of DNA elucidated its function.