* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Human Genome Project wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
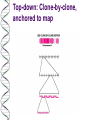
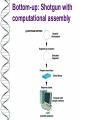
The human genome: sequenced! Obtaining the human genome sequence was a technological breakthrough more than a scientific breakthrough Nonetheless, it is a tremendous advance and provides short cuts to gene identification Genomes are being revealed by sequencing The DNA sequence of the entire haploid set of chromosomes constitutes the genome of an organism (and, more broadly, species). The sequence of many genomes has been (many bacteria, yeast, C. elegans, Drosophila melanogaster, human) or is being (mouse, maize) determined. WHY do we want to determine genome sequence? (minimum genome size necessary for life, evolutionary insights, unravel mysteries of development and disease) HOW do we determine genome sequence? (bottomup, top-down and shotgun methods, contigs, computational methods for sequence assembly and gene recognition) Top-down: Clone-by-clone, anchored to map Bottom-up: Shotgun with computational assembly Human Genomics: New Knowledge Human genomics began as effort to map, identify and clone genes whose mutations caused genetic disease in order to understand the basis of disease and be able to diagnose and treat it more effectively. Even with sequence in hand, there are major problems in gene identification and cloning – need knowledge of map position therefore linkage analysis continues to be of major importance – ultimate goal of reconciling the genetic (linkage) and physical (sequence) maps of chromosomes Another major problem in gene cloning is how to know you have the right gene – importance of mutational analysis and functional tests such as transgenes or gene knockouts in model organisms Genomics: New Applications and New Problems Human genome sequence information makes possible new strategies for: – – – – prenatal testing for genetic disease genetic screening (“DNA chips) forensics gene therapy Pharmacogenetics is an emerging field that unites pharmacology and genetics and aims to get the right drug for the symptom and the individual. Genomics: Summary The study of the human genome allows us to understand how it is put together and gives us resources for gene identification Knowledge of genomes is enabling new technologies and diagnostics.