* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download C-13 Part II Non-Mendelian inheritance
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
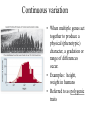
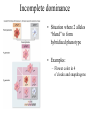
Non-Mendelian inheritance Mendel’s model of inheritance assumes that: -each trait is controlled by a single gene -each gene has only 2 alleles -there is a clear dominant-recessive relationship between the alleles Most genes do not meet these criteria. Polygenic inheritance Polygenic inheritance occurs when multiple genes are involved in controlling the phenotype of a trait. The phenotype is an accumulation of contributions by multiple genes. These traits show continuous variation and are referred to as quantitative traits. For example – human height Continuous variation • When multiple genes act together to produce a physical (phenotypic) character, a gradation or range of differences occur. • Examples: height, weight in humans • Referred to as polygenic traits Pleiotropy Pleiotropy refers to an allele which has more than one effect on the phenotype. This can be seen in human diseases such as cystic fibrosis or sickle cell anemia. In these diseases, multiple symptoms can be traced back to one defective allele. Pleiotropic effects • Occurs when an allele has >1 effect on phenotype • Examples are: – Sickle cell anemia – Cystic fibrosis Incomplete dominance • Situation where 2 alleles “blend” to form hybridized phenotype • Examples: – Flower color in 4 o’clocks and snapdragons Multiple alleles and Blood Groups • ABO Blood groups – – – – IAIA and IAi = type A IBIB and IBi = Type B IAIB and IBIA = Type AB ii = Type O • Rh blood factor • Rh + • Rh- Human Blood types Environmental effects • Allele expression may be affected by environmental conditions • Examples: – Coat color in arctic foxes – Coat color in Himalayan rabbits and Siamese cats • ch allele affected by temp >33 C tyrosinase enzyme inactivates + reduces melanin pigment production Environmental effects on phenotype Epistasis – genes acting together • Situation whereby 1 gene pair affects the expression of a 2nd gene pair • Examples: – Anthocyanin (purple) pigment in corn – Animal coat colors Epistasis (cont’d) • Horse coloration involves 2 or more gene pairings.. • EE or Ee is for black • ee is for red (sorrel) • PLUS other genes can add to base colors • (Bay is AA, EE – black with agouti gene; Buckskin is AA, EE, CcrC – bay with cremello gene, Dun is AA, EE, Dd – bay with dun gene; Palomino is ee, CcrC – sorrel with cremello gene)