* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transcription & Translation
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
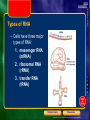
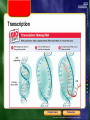
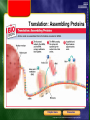
Ch 8-4 Flow of Genetic Information • The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as DNA RNA protein Chapter menu Resources Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. RNA Structure and Function • • • • RNA has the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose RNA has uracil (U) in place of thymine (T) RNA is single stranded RNA is shorter than DNA Chapter menu Resources Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Types of RNA – Cells have three major types of RNA: 1. messenger RNA (mRNA) 2. ribosomal RNA (rRNA) 3. transfer RNA (tRNA) Chapter menu Resources Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Types of RNA 1. mRNA carries the genetic “message” from the nucleus to the cytosol 2. rRNA is the major component of ribosomes 3. tRNA carries specific amino acids, helping to form polypeptides (proteins) Chapter menu Resources Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Transcription • Making RNA from DNA • DNA acts as a template 1. RNA polymerase binds to promoter site 2. 2 strands of DNA unwind 3. Complementary RNA nucleotides are added Chapter menu Resources Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Transcription Chapter menu Resources Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Ch 8-5 Genetic Code • identifies the specific amino acids coded for by each three-nucleotide mRNA codon Chapter menu Resources Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Translation – Making Proteins from RNA – amino acids are assembled from information encoded in mRNA 1. mRNA codons move through the ribosome 2. tRNAs add specific amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain 3. Process continues until a stop codon is reached 4. Newly made protein is released Chapter menu Resources Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Translation: Assembling Proteins Chapter menu Resources Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Translation: Assembling Proteins, continued Chapter menu Resources Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. The Human Genome • The entire gene sequence of the human genome is now known • To learn where and when human cells use each of the proteins coded for in the approximately 30,000 genes in the human genome will take much more analysis Chapter menu Resources Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.