* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
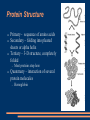
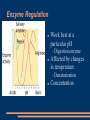
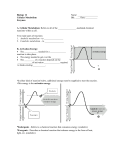
Protein Structure Primary - sequence of amino acids Secondary – folding into pleated sheets or alpha helix Tertiary – 3-D structure, completely folded Most proteins stop here Quaternary – interaction of several protein molecules Hemoglobin 2-4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Enzymes biological catalysts Speed up reactions Without them reactions would occur too slow for life Lower the activation energy Enzymes Enzymes provide a site where substrates can be brought together = Active Site (tertiary) The fit is like a lock and key Enzyme Regulation Work best at a particular pH Affected by changes in temperature Digestion enzyme Denaturization Concentration p. 51 Suggest an explanation for the change at 40 sec. in the control. How does the base affect the enzyme? How does the acid effect the enzyme?