* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BeefIQ12
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Thiomersal controversy wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Whooping cough wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination policy wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Non-specific effect of vaccines wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
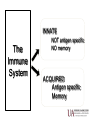
Beef IQ Herd Health – Vaccination & Disease Prevention Jeremy Powell, DVM, PhD Associate Professor University of Arkansas Dept. of Animal Science Basic Principles of Immunology INNATE The Immune System NOT antigen specific NO memory ACQUIRED Antigen specific Memory Innate Immune System • Physical barriers – skin, mm • Chemical protection – tears, saliva, acid • Primary cell types – Myeloid cells • Neutrophils • Eosinophils • Basophils – Macrophages Measured by: Differential cell numbers Chemotactic activity Phagocytic activity Acquired Immune System • Cellular Immune Response – T lymphocytes • TH • TC Longer Lasting • Humoral Immune Response – B lymphocytes (Plasma cells) Antibody production Acquired Immunity • Active immunity – Natural – Artificial • Passive immunity Biologicals and Pharmaceuticals Biologicals and Pharmaceuticals • Biologicals – Made up of bacterins and vaccines – A bacterin/vaccine is a suspension of killed or weakened microorganisms • Killed Vaccine – Has no self-replicating microorganisms • Modified Live Vaccines – Contain microorganisms that have been weakened through culturing and laboratory procedures Biologicals and Pharmaceuticals • Pharmaceuticals: – Are medicinal drugs. – Contain no live or killed microorganisms – Are used to treat a variety of health related conditions – Almost every pharmaceutical has a withdrawal period – Example: Antibiotics such as LA-200 Types of Drug Use • Labeled Use: Using the drug EXACTLY as it is specified on this label. Medicated feed may only be used as directed by the label. Labeled use is legal and the type of use most producers use! • Off Label: The PRODUCER uses drugs on their own in a manner other than what is stated on the label without veterinarian guidance. This is ILLEGAL!! • Extra Label: The VETERINARIAN prescribes a drug to be used in a manner other than what’s on the label. This is legal and is used when a good veterinarian-client-patient relationship exists. Vaccination • Vaccination is a good “protection” tool • Active immunity engaged through vaccinations with biologicals • Vaccination is for prevention of disease – Prevention of disease is cheaper than treatment of disease Points to Ponder • Best Time to Vaccinate?? • When do you need the most protection? • Before disease exposure occurs – Takes 5-7 days for protection with most modified-live vaccines – Killed vaccines require a booster within 2-4 weeks of initial vaccination to obtain adequate protection levels • Don’t expect to vaccinate one day and get protection the next day Points to Consider? • What kind of vaccine? – Killed – Modified-Live – Autogenous • Advantages vs. Disadvantages Killed Vaccines • Viruses, bacterins, toxoids – 1st dose to sensitize – 2nd dose to produce immunity • Two doses required Two dose response curve Killed Vaccine • Advantages – Does not replicate in the animal – Safer to use in pregnant animals • Disadvantages – Most require boosters – Tissue irritation at vaccination site Modified-Live Vaccines • Advantages – Usu. requires one injection – Lower $$$, smaller dose – Less irritation at injection site – Longer immunity • Disadvantages – May cause abortion in pregnant animals – Shouldn’t use on calves nursing preg. cows – Stress from mild form of disease Reasons for Vaccine Failure • Human Error: – Not following directions on the label! – Disinfectant used on syringes – Mixing several products together – Vaccinating at the wrong time – interval More Reasons for Vaccine Failure • Vaccine Factors: – Improper storage of vaccine – Use and restore More Reasons for Vaccine Failure • Host Factors: – Some animals don’t respond More Reasons for Vaccine Failure • Host Factors: – Severe challenge Recommended & Optional Vaccines • Vaccine & est. cost per head: – Recommended: – 5-Way (IBR, BVD, PI3, BRSV) = $1.50 (all) – Blackleg (7-way) = $0.45 (all) – Leptospirosis & Vibriosis = $0.75 (cows) – Optional: – Pasteurella = $2.20 (calves) – Scours = $3.20 (cows) – Pinkeye = $0.85 (all) Why Precondition? • Opportunity to profits • Benefits Both Buyer and Seller – Seller will receive additional value on calves – Buyer realizes improved health and gain performance • Improve the welfare of our cattle Pre-Con Protocol • Requirements differ between sales – Wean Vac vs. VAC 45 • • • • • • • Process 2-4 wks before wean or at wean 5-way: IBR, BVD Types 1&2, PI-3, BRSV Blackleg – 7 way or 8 way Past./H.somnus Dewormer Castrating, dehorn Revac. in 2-6 wks. Economics of Preconditioning Outcome of AR Precon Calf sales Cost & Returns Gross Return Death Loss Labor Veterinary Costs Other costs Hay/Feed/Mineral/Pasture Value/calf $88.99 - $0 - $6.87 - $17.83 - $10.19 - $33.10 Total Net Return $21.00 Check out UA Animal Science Blog: