* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Survey
Document related concepts
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
TV Everywhere wikipedia , lookup
National Broadband Plan (United States) wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
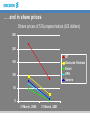
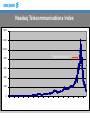
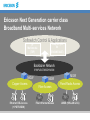
Telecom Markets Trends Raul Lucido vice president strategic marketing & Governmental & regulatory affairs 1995-2000: Unprecedented growth • Internet access boom equals fixed line bonanza • Corporate data needs skyrocket • New revenue streams (US data) – Hosting goes from zero to $2.5 billion – eCommerce services reach $20 billion • Mobile services create a boom – Europe goes from 6% penetration to 54% – Japan goes from 7% to 50% – Hundreds of millions of handsets sold annually There is an irreversible long-term trend in demand for telecoms … 1400 World telecoms revenue As % GDP USD billion Historical 4.0% 3.5% Forecast 1200 3.0% 1000 2.5% 800 2.0% 600 1.5% 400 1.0% 200 0.5% 0 0.0% Source: Analysys As % of GDP 1600 … driven, in part, by technology … 100 000 000 000 000 1 000 000 000 000 10 000 000 000 100 000 000 1 000 000 10 000 100 1 Cooper’s Law states that the number of conversations (voice and data) conducted over a given area, in all of the useful radio spectrum, has doubled every two and a half years for the last 105 years, ever since Marconi discovered radio in 1895 Source: ArrayComm, Martin Copper … and leading to a revolution in the structure of the economy Structural demand for communications and IT Cost to users Cost of basic technologies Short-term demand Telecoms revenue is an accurate indicator of wealth Global telecoms revenue (USD million) per km2 in 1998 Source: Analysys In a world where trade flows look like the Internet … Prices are expected to continue to decline to less than EUR0.05/min Average cost per call minute for a sixline business (1990 EUR): 1991–2001 CAGR reductions on call tariffs of 5–15% in the last ten years Source: Analysys Cutting the Cost Average cost per call minute for an average residential user (1990 EUR): 1991–2001 CAGR reductions on call tariffs of 3–13% in the last ten years We know that demand grows steadily in the long run … 2000 4.0% 1800 3.5% 1600 3.0% 1998 USD billion 1400 2.5% 1200 1000 2.0% 800 1.5% 600 1.0% 400 0.5% 200 0 1985 Source: ITU/Analysys 1990 World telecoms revenue 0.0% 2000 1995 As % GDP … so why have stock markets reacted like this? Deutsche Telekom NASDAQ OTE Source: BigCharts.com Capacity is being reduced … Telecoms job cuts 300 000 250 000 200 000 150 000 100 000 50 000 0 Telecoms manufacturers Source: Telecoms job cuts, Financial Times, September 2001 Telecoms operators … and the change in business climate could last one year or more Over-investment Collapse in values Slow revenues Consolidation Demand and supply match Revenues increase Today 3–4 years 6 months? Investment begins About 1 year A year or so 2001: Operators feel the bust in debt . . . Debt levels of 5 European telcos (millions of Euros) 60,000 50,000 BT Deutsche Telekom Enitel KPN Sonera 40,000 30,000 20,000 10,000 0 Q1 2000 Q1 2001 Source: Company reports . . . and in share prices Share prices of 5 European telcos (US dollars) 250 200 BT Deutsche Telekom Enitel KPN Sonera 150 100 50 0 31 March, 2000 31 March, 2001 Source: Dow Jones, from ADRs listed on NYSE Nasdaq Telecommunications Index 1400 1200 1000 “Hype decisions” 800 600 400 200 2000 01-02-05 1998 99-02-05 1996 97-02-05 1994 95-02-05 1992 93-02-05 1990 91-02-05 1988 89-02-05 1986 87-02-05 1984 85-02-05 1982 83-02-05 1980 81-02-05 1978 79-02-05 1976 77-02-05 1974 75-02-05 1972 73-02-05 71-02-05 0 2002 Main factors creating the hyper-growth and crisis Market Investments Geographical expansion New competitors Good GDP development (US driver) “Technology” Investments Digital Mobile The hypergrowth of the late 1990’s & 2000 Spectrum Internet LH Optics Now • Hyper-growth gone/ • Network spending exceeds • Macroeconomic instability demand in several areas • Signs of subscriber • Increased competition • growth maturity & lower margins Failure in new business models delaying new services Financing constraints (debts, cash,…) Next likely Steps • Many more Operators/SP will go “bankruptcy”, Suppliers? • From Growth focused to Return focused to Profitable Growth focused • Define the core business and divest/close non-core assets • Retain and explore installed customer base • Fast consolidations to create necessary Returns • The “incumbent” telcos will dominate & drive consolidations Consolidation has started. We will see 3 (4) operators per market. The top 20 globally will have more than 80% of revenues. Restructuring Suppliers Main driving forces for the Future Telecom Market Regulation Customer Demands Technology/ Products • Consolidation & Convergence • Economy Development • New Technologies/Services • End-to-end Interoperability/Open standards • Business Models A new communications architecture Today Single-service networks Cable TV Networks Data/IP Networks Wireline Networks Wireless Networks Content Future Multi-services network (carrier class) Applications Service Networks & Application enablers Communication control MGW Connectivity/ Backbone Network Connectivity MGW MGW Access Networks MGW Seamless Interoperable Services - Key to Mass Services 1B (400 M+ Internet) Fixed 1B Mobile End-to-End • E-2-E Connectivity • E-2-E Call completion • E-2-E Applications Business Model Mobile Services - Retail logic Commission (for billing, customer care,…), Revenue sharing Easy to use, Simple pricing, Relevant Services Subscriber charges* Operator/ Service Provider charges Content Provider, Ads Best Practice; i-mode,…) *Entrance fee + Monthly fee + Volume based usage fee SMS Growth, January 2000 to December 2002E Billions/Month 30 SMS was standardized in 1991/1992 25 20 15 10 5 Source; GSM Association 0 Jan-00 Mar-00 Jun-00 Sept-00 Dec-00 Mar-01 Jun-01 Sept-01 Dec-01 Mar-02E Jun-02E Sept-02E Dec-02E Subscriptions (million) Development Sha-mail service, J-Phone ~47% of all subs Launch Nov 2000 Sources: Ovum and Reuters May 2001 Sept 2001 Dec 2001 Aug 2002 Broadband Access has now taken off • Stronger Operator Business Cases • Competitive Technologies Subscribers (Million) 1999 2000 2001 2002E 2003E xDSL 0.7 6.0 17.0 ~33.0 ~52.0 CATV 2.4 9.0 14.0 ~23.0 ~33.0 ~1.0 2.0 ~4.0 ~7.0 Ethernet Source; Dell Oro, etc. Growth of Wireline Broadband Access 12 10 Ethernet metro access 8 USD bill. Fiber Ethernet 6 4 DSL–Ethernet up–link 2 DSL–ATM up–link 0 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 Sources: EU commission, Jefferies & Company, Inc and ECTA, Pioneer Consulting 2001 2009 2010 … Mobile Subscriptions Doubling to 1.8 Billion by 2007 1800 Mobile Subscriptions (million) 1500 1200 Fixed (POTS/ISDN) 900 600 300 Fixed Broadband (Cable, xDSL, LMDS, Fibre) 0 (Year -end) 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 World-wide Operator Services Revenues - “demand” • GDP development/Asia • Broadband, Multi-Media, Mobile & Fixed • “Convergence” • GDP development • Digitalization & SPC 70’s • GDP development • Deregulation 80’s ? • GDP development • Mobile • Internet 90’s 2000 Growth Opportunities • Subscriber Growth • Traffic/Usage Growth • New Communication Services (Voice, Messaging, Imaging/Video,…) • New Content & Applications Our Product Visions; We believe in a main Product Strategy that is based on the following; • Next Generation Networks that is based on an “end-to-end” carrier class “all IP solution” both mobile (3G) and fixed (Broadband) • Seamless migration between today’s networks and subscribers to Next Generation, driven primarily by the large operators • Next Generation “all IP” is based on a single network and multipurpose terminals (or networks) for multiple services (MultiServices) • Open defined standards and APIs, end-to-end Wireless Evolution Analog 1G Wide Area AMPS, NMT, Network (~10km) TACS etc Digital Wideband 2G GSM, PDC TDMA, CDMA 3G WCDMA, EDGE CDMA2000 Local Area Network (~50m) CT1 DECT, PHS WLAN Personal Area Network (~20m) “wire” Infra Red Bluetooth Combined devices 4G Ericsson Next Generation carrier class Broadband Multi-services Network Softswitch Control & Applications IP Multimedia (TSP) Telephony & IN (ENGINE/AXE) Backbone Network IP/MPLS/ATM/SDH/WDM MGW Copper Access Ethernet DSL Access (+ POTS/ISDN) MGW Fibre Access Fiber Ethernet Access MGW Fixed Radio Access LMDS (+W-LAN & 3G) Public Broadband access Backoffice systems Ethernet DSL Access AAA Service Engine Copper Switched Ethernet Ethernet access Service Selection Broadband access server RJ45 e/o Apartment 1 IP network DRG22 RJ45 Apartment 1+n Information e/o Name table Fiber Surveillance camera board Entrance RJ45 Hub e/o Regional Node ELN220 ATM xDSL Access DSLAM Product portfolio strategy – Invest in Next Generation 3-party applications Partners. Ericsson Mobility World Applications Messaging, Browsing, Download, Streaming, Positioning, VPN Services Network/roll-out/ Integration, System Integration, Customer Management, Managed Services Application enablers Broadband Access EDGE NODE/BRAS ENGINE Integral (ATM/IP)/MGW Ethernet Access/DSL LMDS/MINI-LINK BAS Softswitch (TeS/MSC, IP-MM), HSS 2.5/3G Control SDH opto/WDM/DXX, MINI-LINK, Juniper Backbone/Transport Packet core, Circuit core, WCDMA RAN/OSS, EDGE/GSM RAN, CDMA2000, MGW Convergence & Substitutions - Content migration BUSD m-commerce Public Services Positioning Substitutions from other value chains Advertisement Mobile office Media & Music Gaming/Gambling 1000 Messaging Telecom services - GDP development - Business Productivity - Competition - New Services Time 2000 The New Market logic “The ability to learn faster than your competitors may be the only sustainable competitive advantage” Arie de Geus