* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Moons in our Solar System
Survey
Document related concepts
Kuiper belt wikipedia , lookup
Eight Worlds wikipedia , lookup
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Sample-return mission wikipedia , lookup
Giant-impact hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Exploration of Io wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
New Horizons wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
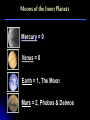
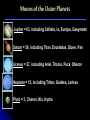
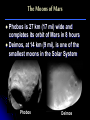
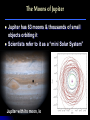
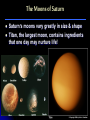
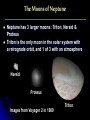
The Moons of Our Solar System How many moons are in our solar system? 1? 9? 61? 159? 159 and counting! Moons of the Inner Planets Mercury = 0 Venus = 0 Earth = 1, The Moon Mars = 2, Phobos & Deimos Moons of the Outer Planets Jupiter = 63, including Callisto, Io, Europa, Ganymede Saturn = 56, including Titan, Enceladus, Dione, Pan Uranus = 27, including Ariel, Titania, Puck, Oberon Neptune = 13, including Triton, Galatea, Larissa Pluto = 3, Charon, Nix, Hydra Comparing the Moons with Earth The Earth’s Moon 384,403 km (238,857 mi) from Earth & 3,476 km (2,160 mi) in diameter 27 days, 7 hours, 43 minutes for rotation and revolution around the Earth Earth’s gravity keeps the same face of the moon permanently turned toward us The Earth’s Moon It’s the only other place in the Solar System that humans have visited. Recently, water ice was discovered at the poles underneath the dusty, cratered surface A “blue moon” is a second full moon in 1 month, & occurs every few years The Earth’s Moon along with Jupiter & 4 of its moons The Moons of Mars Mars has 2 moons: Phobos & Deimos In Greek, Phobos means “fear” & Deimos means “dread”; they are the sons of Mars, the god of war These moons are heavily cratered & probably captured objects The Moons of Mars Phobos is 27 km (17 mi) wide and completes its orbit of Mars in 8 hours Deimos, at 14 km (9 mi), is one of the smallest moons in the Solar System Phobos Deimos The Moons of Jupiter Jupiter has 63 moons & thousands of small objects orbiting it Scientists refer to it as a “mini Solar System” Jupiter with its moon, Io The Moons of Jupiter In 1610, Galileo was the first person to discover the largest moons of Jupiter: Ganymede, Callisto, Io, and Europa Since then, several spacecraft have examined these “Galilean Satellites” closely Ganymede Callisto Io Europa The Moons of Saturn Saturn has 56 moons The Cassini spacecraft discovered 12 new moons orbiting the planet in 2005 alone Saturn Cassini spacecraft The Moons of Saturn Saturn’s moons vary greatly in size & shape Titan, the largest moon, contains ingredients that one day may nurture life! The Moons of Uranus Uranus has 27 moons Many of them are icy, without an atmosphere or magnetosphere The rings of Uranus and its many moons The Moons of Uranus The 5 largest were discovered in the 19th and 20th centuries: Titania, Oberon, Umbriel, Ariel & Miranda Titania Oberon Umbriel Ariel (images not to scale) Miranda The Moons of Neptune Neptune has 13 moons, 3 of which were discovered in 2002, 2 more in 2003 In 1989, Voyager 2 discovered 6 moons not visible from Earth All of Neptune’s moons are composed of rock & ice, but little else is known about them The Moons of Neptune Neptune has 3 larger moons: Triton, Nereid & Proteus Triton is the only moon in the solar system with a retrograde orbit, and 1 of 3 with an atmosphere Nereid Proteus Images from Voyager 2 in 1989 Triton The Moons of Pluto Pluto has 3 moons: Charon, Nix, and Hydra Charon and Pluto have a mutually synchronous orbit, meaning they always show the same face to each other For the Greeks, Charon was the boatman who carried dead souls to the underworld, ruled by Pluto Pluto Charon The Moons of Pluto At 1,186 km (737 mi), Charon’s diameter is little more than half of Pluto’s; no other moon in our solar system is so close in size to its planet Charon appears to be covered by water ice, differing from Pluto’s surface of frozen nitrogen, methane & carbon dioxide Hubble Space Telescope image of Pluto (left) & Charon The Moons of Pluto In November 2005, astronomers discovered two new moons of Pluto: Nix and Hydra. Both moons are much farther away from Pluto than Charon, and many times smaller. Nix is named after the Greek goddess of night, Charon’s mother. Hydra is a beast that guarded Pluto’s underworld. Moons of Our Solar System Earth is not the only planet with a moon. At least 159 moons with craters, volcanoes & other spectacular features exist in our solar system. Which ones are your favorites?