* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Reproduction - Fulton County Schools
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
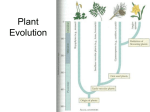
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
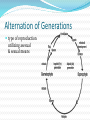
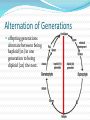
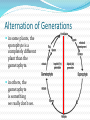
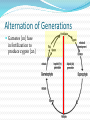
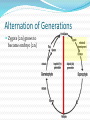
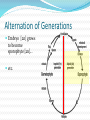
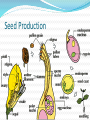
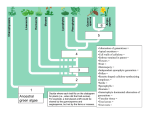
Unit 6 – Lecture 6 Alternation of Generations type of reproduction utilizing asexual & sexual means Alternation of Generations offspring generations alternate between being haploid [1n] in one generation to being diploid [2n] the next. Alternation of Generations in some plants, the sporophyte is a completely different plant than the gametophyte. in others, the gametophyte is something we really don’t see. Alternation of Generations Sporophyte [2n] produces spores [1n] through meiosis sporophyte is the typical “adult plant” that we see Alternation of Generations Spores [1n] produce gametophytes [1n] through mitosis Alternation of Generations Gametophyte [1n] produces gametes [1n] through mitosis Alternation of Generations Gametes [1n] fuse in fertilization to produce zygote [2n] Alternation of Generations Zygote [2n] grows to become embryo [2n] Alternation of Generations Embryo [2n] grows to become sporophyte [2n]… etc. Alternation of Generations non-vascular and non-seed plants MUST have water to reproduce. flagellated sperm must swim to egg gametophyte can be very small, but visible – 1cm or less. Other Asexual Reprod Methods vegetative reproduction – new plant forms from existing plant part (roots) fragmentation – new plant forms from a cutting of the original plant. Seed Plants are vascular… two varieties: gymnosperm – produce cones angiosperm – produce flowers Angiosperms produce flowers and seeds inside of a fruit petals, pistil, stamen, etc. petals attract pollinators fruit attracts organisms which can spread seeds Angiosperms Angiosperms Angiosperms are either monocot or dicot cotyledon – the seed “leaves” or sides / food supplies don’t need to know these directly: have different types of xylem & phloem have different types of veination have differences in petal arrangement Seed Production Germination germination – zygote growing into new plant requirements: water suitable temperature oxygen time Germination germination – zygote growing into new plant requirements: light other: freezing – apples soaking in salt water – coconuts fire – many conifers cannot be halted