* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Terminology: The Parts of a Plant
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
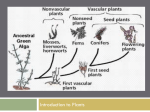
Matthew Boggs Aaron Seigler Victor Makali Gordon A seed is a fertilized, ripened ovule of a gymnosperm or angiosperm. A fruit is a ripened and mature ovary containing seeds. Ovule- In plants, a structure that contains a gametophyte and, within the gametophyte, an egg; when it matures, an ovule becomes a seed. Ovary- Any female organ, that produces an egg. Angiosperm- Plants with ovules, enclosed in an ovary. Gymnosperm- a vascular plant whose seeds are not in an ovary. 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Seed Coat Cotyledon- an embryonic organ that stores and digests reserve materials. Shoot Apex Root Apex Endosperm- contains stored nutrients for the developing embryo. 1) 2) 3) Exocarp Mesocarp Endocarp The “Pericarp” is the collective term for the above components of a fruit. Not all plants produce seeds. • Gametophyte: the alternation of generations, the multicellular haploid phase that produces the gametes. • Sporophytes: the alternation of generations, the diploid phase that produces the spores. • The purpose of a fruit is to provide protection and nutrients as well as help with dispersal. The “above ground” part of the plant, known as the shoot system starts to grow once the root system as established secure anchoring. 1) Stems 2) Leaves 3) Nodes and Internodes - a node is the point on a stem where a leaf is or was attached. - an internode is the region between two nodes. A plant will grow towards or with a stimulus, i.e. a plant will grow toward a source of light. The upper parts of the plant depend on the roots to provide water and dissolved minerals collected from the soil. The root depends on the upper part of the plant to produce sugars and other organic substances through photosynthesis. The Shoot System and Root System are connected through two sets of vascular tissues(Xylem and Phloem) that transport resources back and forth. Xylem- the vascular tissue that conducts/transports water and dissolved minerals in plants. Phloem- the vascular tissue that conducts/transports dissolved sugars and other organic compounds in plants. Sadava, David, David Hillis, William K. Purves, H. C. Heller, and Gordon H. Orians. Life : The Science of Biology. 8th ed. Boston: W. H. Freeman & Company, 2006. “Plants Know the Way to Grow.”Fast Plants. 1995. http://www.fastplants.org/pdf/activities/ know_the_way.pdf