* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2. No vascular tissue
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
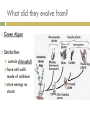
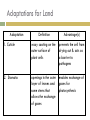
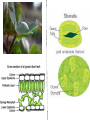
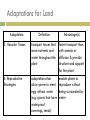
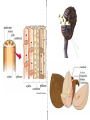
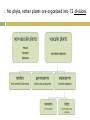
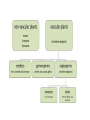
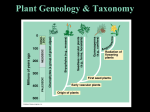
Introduction to Plants What is a Plant? Multicellular Eukaryotic Photosynthetic Has cell walls containing cellulose Lacks mobility What did they evolve from? Green Algae Similarities contain chlorophyll have cell walls made of cellulose store energy as starch Original Habitat The simplest plants live surrounded by water because water satisfies many of their needs: prevents cells from drying out gives structural support provides nutrients helps with spore dispersal and meeting of sex cells With time, plants adapted to live on land Adaptations for Land Adaptation Definition Advantage(s) 1. Cuticle waxy coating on the outer surface of plant cells prevents the cell from drying out & acts as a barrier to pathogens 2. Stomata openings in the outer enables exchange of layer of leaves and gases for some stems that photosynthesis allows the exchange of gases Adaptations for Land Adaptation Definition Advantage(s) 3. Vascular Tissues transport tissues that move nutrients and water throughout the plant faster transport than with osmosis or diffusion & provide structure and support for the plant 4. Reproductive Strategies adaptations that allow sperm to meet egg without water (e.g. spores that have waterproof coverings, seeds) enable plants to reproduce without being surrounded by water Plant Life Cycle The lives of plants consist of two alternating stages, or generations: a gametophyte generation and a sporophyte generation. The stage that produces gametes (sperm and eggs) is the gametophyte generation. It is haploid. The stage that produces spores is the sporophyte generation. It is diploid. Plant Life Cycle One generation is dominant over the other. This means that it is larger and lasts longer. In most plants, the diploid sporophyte generation is dominant. In mosses, the gametophyte dominates. How are Plants Classified? No phyla, rather plants are organized into 12 divisions. Non-Vascular Plants Include mosses, liverworts, & hornworts 1. Do not have true roots, stems and leaves - absorb water through cell walls; water moves via osmosis. 2. No vascular tissue - no xylem and phloem to transport water and nutrients Non-Vascular Plants 3. Small size - no support from vascular tissues 4. Depend on water for reproduction - water is needed for the sperm to swim to the egg Vascular Plants 1. Have true roots, stems and leaves 2. Contain vascular tissue - xylem transports water - phloem transports food and nutrients - run continuously through the roots, stems and the leaves Vascular Plants 3. Larger size - vascular tissues provide support against gravity 4. Cuticle - reduces water evaporation from leaves and some stems Seedless Plants Most plants have vascular tissue but may or may not produce seeds. Ferns, horsetails, and club mosses are seedless vascular plants that reproduce by spores. Gymnosperms Plants that reproduce by seeds are divided into 2 groups: gymnosperms and angiosperms. Gymnosperms have "naked" seeds usually protected by cones. They include the evergreens. Angiosperms Angiosperms are flowering plants whose seeds are produced and protected within fruit. Further divided into monocots and dicots.