* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kinetic Theory
Survey
Document related concepts
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Grand Unified Theory wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
ALICE experiment wikipedia , lookup
Theory of everything wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
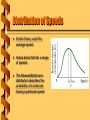
Kinetic Theory Microscopic Analysis 1) 2) 3) 4) The behavior of a gas should be described by the molecules. The gas consists of a large number of identical particles of mass m. The particles have negligible size and no internal structure. The particles are moving in random dirctions with speeds independent of direction Collisions between particles and with the walls are perfectly elastic. Collision Force L Fx Follow a collision with a wall perpendicular to x. Particle has mass m and a velocity vx. • Strike the wall: Dt = 2L/vx. • Impulse: Dp = 2mvx. v m The force from one particle: mvx2 Dp 2mvx F Dt 2 L / vx L Pressure Force The pressure on the wall comes from all the particles. 2 Fx Fxi m vx P A A AL The volume is V = AL. Find the value for N particles. L A P m v x2 AL mN V 2 v x N mN 2 vx V Three Dimensions V The pressure come from all three dimensions, and is equal in all three. v 2 v x2 v y2 v z2 3v x2 P N Relate the pressure to the average speed. mN v 2 2 N 1 2 P ( 2 mv ) V 3 3V Theory Match V P The expression from a particle level relates the average kinetic energy. PV N N 2 1 2 ( 2 mv ) 3 This almost matches the ideal gas law. PV N (kT ) Temperature as Energy For the particle-level theory to match the experimental law we equate them. 2 1 2 PV N ( 2 mv ) N (kT ) 3 1 2 mv 2 32 kT This is kinetic theory. Temperature measures the average kinetic energy. Average Energy What is the average energy of an air molecule at room temperature (293 K)? What is average speed for a nitrogen molecule (28 g/mol)? Energy directly relates to temperature. (3/2)kT = 6.07 x 10-21 J. To get the speed requires the mass. m = (0.028 kg/mol) / (6.022 x 1023 /mol) = 4.65x10-26 kg 3kT v 511 m/s m Distribution of Speeds Kinetic theory used the average speed. Actual atoms fall into a range of speeds. The Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution describes the probability of a molecule having a particular speed. Real Gases The assumptions for kinetic theory are approximately true. • Non-zero molecular size • Non-zero force between molucules For the Van der Waals force in air, the effect is about 1% difference from an ideal gas. next