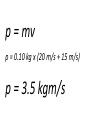* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 6 Pretest
Routhian mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Tensor operator wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Special relativity wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Uncertainty principle wikipedia , lookup
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Accretion disk wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum operator wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Pre-AP Physics Ch 6 Momentum Pretest 1. Which of the following is an example of a visible change in momentum? A) A car runs into a brick wall. B) A fly hits the windshield of a car. C) An outfielder catches a baseball. 1. Which of the following is an example of a visible change in momentum? A) A car runs into a brick wall. B) A fly hits the windshield of a car. C) An outfielder catches a baseball. 2. A roller coaster climbs up a hill at 4 m/s and then zips down the hill at 30.0 m/s. The momentum of the roller coaster: a. is greater up the hill than down the hill b. is greater down the hill than up the hill c. remains the same throughout the ride d. is zero throughout the ride 2. A roller coaster climbs up a hill at 4 m/s and then zips down the hill at 30.0 m/s. The momentum of the roller coaster: a. is greater up the hill than down the hill b. is greater down the hill than up the hill c. remains the same throughout the ride d. is zero throughout the ride 3. An ice skater initially skating at a velocity of 3 m/s speeds up to a velocity of 5 m/s. The momentum of the skater: a. decreases b. increases c. remains the same d. becomes zero 3. An ice skater initially skating at a velocity of 3 m/s speeds up to a velocity of 5 m/s. The momentum of the skater: a. decreases b. increases c. remains the same d. becomes zero 4. The change in an object’s momentum is equal to: a. the product of the mass of the object and the time interval. b. the product of the force applied to the object and the time interval. c. the time interval divided by the net external force. d. the net external force divided by the time interval. 4. The change in an object’s momentum is equal to: a. the product of the mass of the object and the time interval. b. the product of the force applied to the object and the time interval. c. the time interval divided by the net external force. d. the net external force divided by the time interval. 5. A softball with a mass of 0.11 kg moves at a speed of 12 m/s. Then the ball is hit by a bat and rebounds in the opposite direction at a speed of 15 m/s. What is the change in momentum of the ball? a. -1.3 kg•m/s b. -1.6 kg•m/s c. -0.33 kg•m/s d. -3.0 kg•m/s 5. A softball with a mass of 0.11 kg moves at a speed of 12 m/s. Then the ball is hit by a bat and rebounds in the opposite direction at a speed of 15 m/s. What is the change in momentum of the ball? a. -1.3 kg•m/s b. -1.6 kg•m/s c. -0.33 kg•m/s d. -3.0 kg•m/s 6. Which of the following statements about the conservation of momentum is NOT correct? a. Momentum is conserved for a system of objects pushing away from each other. b. Momentum is not conserved for a system of objects in a head-on collision. c. Momentum is conserved when two or more interacting objects push away from each other. d. The total momentum of a system of interacting objects remains constant regardless of forces between the objects. 6. Which of the following statements about the conservation of momentum is NOT correct? a. Momentum is conserved for a system of objects pushing away from each other. b. Momentum is not conserved for a system of objects in a head-on collision. c. Momentum is conserved when two or more interacting objects push away from each other. d. The total momentum of a system of interacting objects remains constant regardless of forces between the objects. 1. What does it mean to say that momentum is conserved? The total momentum of a system does not change unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. 2. A rubber ball with a mass of 0.10 kg moves at 20 m/s. It hits a brick wall and rebounds at a speed of 15 m/s in the opposite direction. What is the change in momentum of the ball? p = mv p = 0.10 kg x (20 m/s + 15 m/s) p = 3.5 kgm/s 3. How is the momentum of a running child affected when he runs into a stone wall and stops? The child’s momentum decreases to zero. 4. How are impulse and momentum related? Impulse is equal to the change in momentum. Ft = Dmv 5. A 40.0 kg boy and a 30.0 kg girl are each floating on inflatable swimming pool mats. The girl pushes the boy, who moves away at a speed of 3.0 m/s. What is the girl's speed? Dmv = Dmv 40 kg x 3 m/s = 30 kg x v 120 kgm/s = 30 kg x v v = 4 m/s