* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organelles of the Cell
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
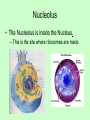
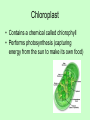
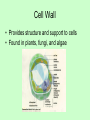
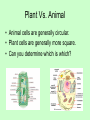
Organelles of the Cell Each organelle has a specialized function in the cell Plant vs. Animal Cells • Plant and Animal cells are similar in many ways, but have a few differences. • The following organelles exist in both plant and animal cells. Cell Membrane • The Cell Membrane surrounds the cell. • The membrane is semi-permeable, which means it regulates what substances enter and exit the cell. • It is made up of proteins and lipids. Nucleus • The Nucleus is the control center of the cell. – It stores the cell’s genetic information (in Chromosomes) – It makes copies of the Chromosomes – It usually exists in the center of the cell. Nucleolus • The Nucleolus is inside the Nucleus. – This is the site where ribosomes are made Cytoplasm • The Cytoplasm fills the cells. – It is a jelly-like substance that supports and protects the organelles. Mitochondria • The Mitochondria is the “battery” of the cell. – It makes energy for the cell to use – All of the parts of the cell need energy to do work. – Mitochondria have a lot of folds in their membrane to provide lots of places for sugars to be turned into useable energy for the cell. Ribosome • The Ribosome is the production line of the cell. – Gets a copy of the instructions from the nucleus. – Makes a protein from the instructions. – Cells contain many ribosomes. – Ribosomes are small organelles that exists all over the cell. Endoplasmic Reticulum • The Endoplasmic Reticulum is the Conveyor belt of the cell. – It is the internal membrane system for the cell – The ribosomes can attach to the ER to do their work. - The ER moves proteins and other substances throughout the cell. Golgi Body • The Golgi Body is the packager of the cell. – Adds small things to the protein. – Checks the protein to make sure it is correct. – Packages proteins and releases cellular secretions The ER and Golgi work together. Lysosome • The Lysosome is the Recycler of the cell. – To “Lys” means to cut. – Lysosomes use digestive enzymes to cut proteins into their parts. – The cell can then use these parts again. Vacuole • Stores food, water, and waste. • Plant cells have one large vacuole • Animal cells have many small vacuoles Plant Cells • The following Organelles exists only in plant cells. Chloroplast • Contains a chemical called chlorophyll • Performs photosynthesis (capturing energy from the sun to make its own food) Cell Wall • Provides structure and support to cells • Found in plants, fungi, and algae Plant Vs. Animal • Animal cells are generally circular. • Plant cells are generally more square. • Can you determine which is which? Organelles of the cell Venn Diagram • Draw a Venn Diagram to compare plant and animal cells. • Each section must include at least 3 pieces of information.