* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit B: Cell structure
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
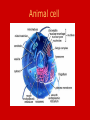
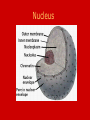
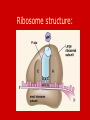
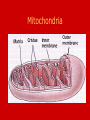
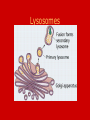
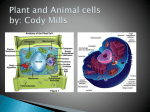
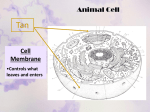
Unit B: Cell structure Animal cell Liver Cell Cell membrane Nucleus Nucleus Nuclear pores FUNCTIONS OF NUCLEUS: • Nuclear membrane/envelope bilayer, separates and contains nuclear contents (DNA). • Nuclear pores: allow mRNA out of nucleus, nucleotides, nutrients & enzymes in. They are made from protein. • Chromatin: Protein & DNA; form chromosomes when cell divides. • Nucleolus:contains rRNA and Ribosomal proteins. The Endoplasmic Reticulum: ER • Rough E.R. • Smooth E.R. • Studded with ribosomes • Site of protein synthesis for proteins meant for export • Phospholipids made here • Detoxifies poisons (found in liver cells) • Synthesize steroids Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes Function of Ribosomes • Made from two protein subunits and rRNA • Some are free, found alone in cytoplasm • Others are attached to the RER • Translation of mRNA into polypeptides or PROTEIN SYNTHESIS! Ribosome structure: Mitochondria Function of Mitochondria: • Cellular Respiration converts energy in Glucose to ATP • C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O + 38 ATP • Found in large numbers in energetic cells (sperm cells, muscles etc.) Golgi apparatus Looks like a series of flattened sacules. Appears close to the cell membrane. Golgi •Packages, modifies and stores molecules. •Forms transport or secretory vesicles •Involved in export of proteins through exocytosis. •Draw diagram page 2 in green book exocytosi.ram Lysosomes Lysosomes: • Contain hydrolytic enzymes (help to perform hydrolysis) for digesting molecules. • These special vacuoles merge with another molecule containing vacuole for cell digestion. • Called “suicide sacs”, contents could destroy cell! Microtubules, cytoskeleton Cytoskeleton • Many protein filaments (actin filaments and microtubules) help organize and anchor cell parts. cilia Cilia and flagella microtubule arrangement 9+2 Function of cilia and flagella: Cilia: •Line the respiratory passages and sweep mucus upwards. •Line the oviducts to transport ovum to uterus •Flagella: Propel sperm towards the ovum.