* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 6 - MrsAllisonMagee
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
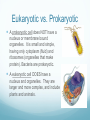
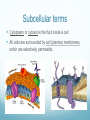
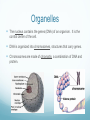
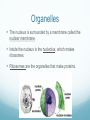
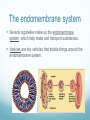
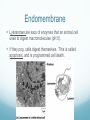
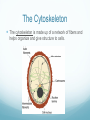
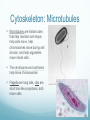
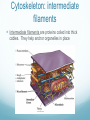
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Basic Definitions A cell is the basic unit of life. All living things are made of cells. Inside cells are organelles, which are small, membrane bound structures that have specific jobs. Cells are small because nutrients and water must be able to get to all parts of the cell (low surface area to volume ratio) Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic A prokaryotic cell does NOT have a nucleus or membrane bound organelles. It is small and simple, having only cytoplasm (fluid) and ribosomes (organelles that make protein). Bacteria are prokaryotic. A eukaryotic cell DOES have a nucleus and organelles. They are larger and more complex, and include plants and animals. Subcellular terms Cytoplasm or cytosol is the fluid inside a cell. All cells are surrounded by cell (plasma) membranes, which are selectively permeable. Organelles The nucleus contains the genes (DNA) of an organism. It is the control center of the cell. DNA is organized into chromosomes, structures that carry genes. Chromosomes are made of chromatin, a combination of DNA and protein. Organelles The nucleus is surrounded by a membrane called the nuclear membrane. Inside the nucleus is the nucleolus, which makes ribosomes. Ribosomes are the organelles that make proteins. The endomembrane system Several organelles make up the endomembrane system, which help make and transport substances. Vesicles are tiny vehicles that shuttle things around the endomembrane system. Endomembrane: the ER The endoplasmic reticulum is a series of membranes that make up almost half of the cell. There are two types: Rough ER: has ribosomes on the surface; makes proteins and membranes Smooth ER: has no ribosomes on it; makes lipids, carbs, enzymes, and detoxifies drugs and poisons. Endomembrane The Golgi Apparatus (Golgi Body) is like the cell’s UPS: it manufactures, stores, sorts, and ships products made by the ER to other parts of the cell. Endomembrane Lysosomes are sacs of enzymes that an animal cell uses to digest macromolecules (pH 5). If they pop, cells digest themselves. This is called apoptosis, and is programmed cell death. Endomembrane Vacuoles are large, hollow organelles. They can be Food vacuoles: used to store and digest cellular food Contractile vacuoles: pump excess water from cells, help propel them through liquid Central vacuole: found in plant cells, store water. Are surrounded by a membrane called the tonoplast. Review of the Endomembrane System Energy Organelles The mitochondria is found in plant and animal cells. It is the site of cellular respiration, the power house of the cell, and makes energy (ATP) from sugar and oxygen. Inner membrane is called the cristae Inside the cristae is a compartment called the matrix. Energy Organelles The chloroplast is found ONLY in plant cells, it converts light energy into chemical energy (ATP). The fluid in the chloroplast is called the stroma Thylakoids (look like poker chips) are stacked in piles called grana Energy Organelles Peroxisomes contain enzymes that transfer hydrogen from various substances to oxygen, makes hydrogen peroxide H2O2. These break down fatty acids and detoxify poisons The Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is made up of a network of fibers and helps organize and give structure to cells. Cytoskeleton: Microtubules Microtubules are hollow tubes that help maintain cell shape, help cells move, help chromosomes move during cell division, and help organelles move inside cells. The centrosome and centrioles help move chromosomes Flagella are long tails, cilia are short hair-like projections, both move cells Cytoskeleton: microfilaments Microfilaments are double stranded filaments that help maintain cell shape, are involved in muscle contraction, and help cells divide and move. Actin is a protein that helps muscles move Cytoskeleton: intermediate filaments Intermediate filaments are proteins coiled into thick cables. They help anchor organelles in place Outside the Cell Plant cells have cell walls made of cellulose. They protect and support the cell, and regulate water balance. Plasmodesmata are holes in cell walls that allow water and nutrients to be exchanged. Animal cells have intercellular junctions for this function