* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Bio - Chapter 6.4 Presentation
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
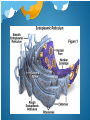
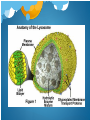
Intro to Endoplasmic Reticulum Network of of membranous tubules and sacs called cisternae Takes up more than half of total membrane in most eukaryotic cells. ER Membrane separates lumen (interior cisternal space) and from cytosol. Two distinct regions: Smooth ER and Rough ER. Smooth ER Functions Lipid Synthesis Sex hormones Carbohydrate metabolism Drug/Poison Detoxification Hydroxyl groups changing solubility Habituation Calcium ions In muscle cells, these trigger contractions Rough ER Functions Protein and Membrane synthesis Ribosomes covering Rough ER secrete proteins Folded into lumen Later transported by vesicles Ex. Insulin Membranes made for itself are later transported to other endomembrane systems Golgi Apparatus Functions Compacts and stores proteins Vesicles Molecular Identification Made of cisternae Cis and Trans faces Cis serves as bridge w/ER Trans makes vesicles for transport to other cell regions Modifies proteins Cisternae between cis and trans faces Lysosomes Membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes Digests macromolecules Autophagy and Phagocytosis Auto- lysosomes digest/recycle inner cell material Liver Cells Phagocytosis- cell ingests other cell A cell’s stomach, acid and all. Nutrients pass into cytosol Vacuoles Food Used to digest other cells, fuses w/lysosomes. Contractile Pump excess H2O out of cell (usually freshwater protists) Central Cell sap inside, different than cytosol Holds reserve organic and inorganic compounds, metabolic byproducts, pigmentation, and toxins. More H2O in vacuole, bigger plant cell